What is the cold/warm/hot start in GNSS module?




It is found that it takes some time for a enabled GPS module to obtain signal from enough satellites to determine its location accurately. So why?
Before answering this question, firstly we have to know how many satellites need to be tracked to output positioning data.
The basic positioning principle of GNSS is that the satellite continuously broadcast ephemeris messages that enable the user’s GNSS receiver to determine the satellite’s antenna position when the measurement signal was broadcast (in cartesian X, Y, Z coordinates). Therefore, at least 4 satellites to achieve precise positioning information. The basic requirements are as follows:
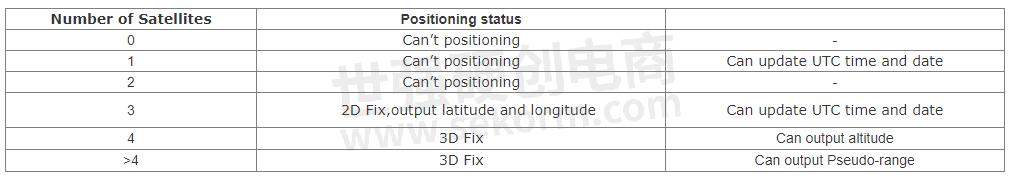
Generally, after the positioning module is powered on, it uses the antenna to track satellites, then parses transmitted message to generates ephemeris internally, finally calculates and obtains current positioning. Due to the difference in signal strength and receiver’s computing capability, it usually takes tens of seconds to several minutes to get fixed solutions. In this process, searching for stars and generating ephemeris files takes the longest. The length of the positioning time is also related to the way the module is started and the environment it is in.
The GPS within the module can boot up in one of three modes based on speed of positioning: Cold Start, Warm Start and Hot Start.
Cold start
Cold start means forced boot by hardware. After cold start, the module clears all historical information and there’s no stored ephemeris in the local flash. GNSS module can not perform normally and needs to re-acquire coordinate data when the satellite parameters are lost, or the existing parameters are too different from the received satellite parameters. However, it will take a long time to regain the data since the loss of previous satellite information. For example, when 1) module is used for the first time, 2) ephemeris information is lost due to the exhaustion of the battery, 3) the module is restarted after restoring the factory settings. Generally, it takes more than 30 seconds to establish a position.
Warm start
Warm start refers to the boot exceeding 2 hours since the last positioning. In this situation, the module has stored the satellite position, almanac and UTC time calculated at the last moment, but the previously stored ephemeris has changed, which means the saved content is inconsistent with the current visible satellite data and and the previous satellites cannot be received as time is more than two hours. Thus, GNSS module needs to re-searching for stars to to complete the location information. Therefore, the speed of warm start is between cold start and hot start. Nowadays, warm start is gradually canceled as the mode parameters between the cold start and the warm start can be very close with the prior art.
Hot start
The GPS starts up in this mode when module has not been moved too much at the place where it was shut down last time and time is within at least 2 hours to shut down so that modules keep the record of the position, almanac and UTC time of the last calculated visible satellite. After restarting, The module can obtain and calculate the positioning based on the previously saved content. In this mode, the module rapidly obtain the current positioning through software, like performing some pre-start saving and restarting command.
SinoGNSS(by ComNav technology Ltd.) K8 GNSS module: cold start within 20s
The latest K8 series modules built in high-precision SoC chips with optimized baseband satellite tracking algorithm, which can capture satellite signals in a short period of time and more satellites are computed, so that availability, accuracy and reliability are improved in a large extent, especially in complex environment. Additionally, the more channels a GNSS module has, the more satellites it can track. The baseband processing unit decodes the satellite signal and obtains the satellite message. The signal of each satellite needs a separate channel for processing, for example if there are 100 satellites and 2 frequency bands, it needs 200 channels to effectively process this information. The embedded SoC chip has 965 channels in total, which can process the current and future GNSS signals.
The fixed time of K8 series modules for a cold start is within 20s in the open environment, which largely contributes to it’s capability of tracking B2b signal with the optimized baseband satellite tracking algorithm in GNSS chip. As the period of B2b broadcast ephemeris is short, using the telegram information parsed by B2b can quickly collect satellite ephemeris and satellite clock information, so that the cold start time is shorter.
- |
- +1 赞 0
- 收藏
- 评论 0
本文由深蓝的鱼转载自ComNav technology News,原文标题为:What is the cold/warm/hot start in GNSS module?,本站所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源,不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
相关推荐
【技术】GNSS模块/板卡数据质量快速评估方法详解:零基线法和原始数据质量分析法
随着北斗三号的全球组网以及LBS、物联网和智能驾驶的发展,GNSS模块开始向小型化、集成化方向发展,GNSS应用也从专业应用走向大众应用。对用户而言,GNSS仍具有较强的专业性,在使用中难免会遇到各类问题。本文介绍GNSS模块的快速评估方法供大家参考。
The Magic Behind RTK: Delivering Unparalleled Positioning Precision
In today‘s advanced technological era, accurate positioning has become a cornerstone for numerous applications, ranging from agriculture to construction and beyond. But what exactly is RTK, and how does it stand out in the vast landscape of satellite navigation systems?
Recommend Commands for System Integration
As more and more of users integrate ComNav high precision GNSS modules into various applications, such as Robotics, UAV, Surveying and Mapping, Precision Agriculture, Automatic Driving, to improve the system‘s debuggability, it is advisable to reserve a port for communication with the internal module in ComNav‘s high precision GNSS modules. This allows users to easily view module information at a later time and access the data for analysis when needed.
司南导航(Comnav Technology)K8系列北斗/GNSS高精度定位模块选型指南
目录- 公司介绍 核心技术 K系列模块对比表 高精度模块 数传模块 北斗RDSS短报文通信模块 行业应用 服务与支持 生产与管理
型号- EVK-QD302,CRU,K8-U70,RD02,K803+U70,CDL7,K系列,QD302,K803_EK0405,EVK-K823,U703,EVK-K803,K803_EK0407,K801,K823,W803,GBAS,K802,U70,K827,K803,K823_EK0407,K807,K8系列,K823+U70,K803_EK0610
K系列OEM板用户指南
描述- 本指南为ComNav Technology K系列OEM板提供了安装、配置和操作说明。指南涵盖了OEM板的概述、评估套件、相关文档、安装指南、CRU软件配置、工作模式配置、常用命令和固件更新等内容。指南详细介绍了如何使用CRU软件进行OEM板的配置,包括状态检查、命令接口、NTRIP配置、数据记录配置和数据管理。此外,还介绍了不同工作模式的配置,如平滑模式、SBAS模式、RTK模式、RTD模式和移动基线模式。最后,指南还提供了常用命令的说明。
型号- K728,K706,K726,K803,K705,K708,K-SERIES,K823,K700,K8-SERIES
【经验】深度解析GNSS模块的冷/热启动是什么?
GNSS的基本定位原理是卫星不间断地发送自身的星历参数和时间信息,用户在接收到这些信息后,经过计算得出模块的三维位置、三维方向以及运动速度和时间信息。信号强度、芯片运算能力存在差异,将模块定位时长按快慢进行排序:热启动>温启动>冷启动。
实现毫米级实时定位,司南导航提供车规级高精度GNSS定位模块
2022年5月1日,司南导航(股票代码:833972)与世强达成合作,授权世强代理旗下全线产品,为用户提供全方位、多领域的高精度北斗芯片和高精度GNSS芯片、板卡、终端和系统解决方案。司南导航产品已全线上线平台,搜索“司南导航”即可获取更多产品资讯。
K802 GNSS模块
描述- K802是一款尺寸为22mm×17mm×2.8mm的GNSS模块,具备多系统支持、高精度定位和低功耗等特点。该模块采用ComNav的QUANTUMⅢSoC芯片,适用于专业级应用,支持GNSS+INS导航,并具备RTK定位功能。
型号- K SERIES,K802
司南导航(Comnav Technology)GNSS模块选型表
目录- GNSS模块
型号- K827,K823E,K8,K803‐U70,K9,K803_EK0405,K803 LITE‐QD302,EVK‐K823,EVK‐K803,K802S,K823‐U70,K803_EK0407,K11,K10,K801,K823,K802,K803LITE,K803,K823_EK0407,K825,K803S5,K807,K825S,K827S,K803_EK0610,K801S,K823S
K803 GNSS模块
描述- K803 GNSS模块是一款小型、高性能的定位模块,具备多系统、多频段支持,适用于多种环境下的精确定位。该模块采用ComNav的Quantum III SoC芯片,具有低功耗、高精度等特点,适用于隧道、建筑物和森林等复杂环境。
型号- K803,K SERIES
全国产单北斗系统全频点RTK定位模块K803G、K823G,具有低延迟和抗干扰等特点
K803G和K823G GNSS Module 是上海钦天导航技术有限公司基于具有完全自主知识产权的Quantum lll开发的全国产单北斗系统全频点RTK定位模块,支持BDS-2、BDS-3卫星系统信号跟踪,适用于测量测绘、机器人、地基增强等领域。
K803 GNSS Module Product Specification(K803 GNSS模块产品规范)
描述- K803 GNSS模块是一款基于自主研发SoC的高精度定位OEM模块,具备小型化、多系统和多频点的特点。它支持GPS、BDS-2、BDS-3、GLONASS、Galileo、SBAS和QZSS等多个卫星系统,主要用于对尺寸、重量和功耗有严格要求的无人机和手持设备。
型号- K803
K801 GNSS开发板
描述- K801 GNSS Development Board是一款由ComNav Technology推出的高性能、低成本GNSS定位模块,适用于厘米级和分米级高精度定位需求,适用于物联网、智能驾驶、无人机和机器人等消费市场及解决方案。
型号- K SERIES,K801
【应用】司南导航AG360北斗农机自动驾驶系统助力农机导航,定位误差不超过±2.5厘米且支持AB线共享作业
司南导航的农机导航产品,不仅操作简单、信号稳定、适配广泛,而且还提供24小时售后服务。让农业生产更加高效、节省成本,同时保证农业生产的质量和产量,为农业生产带来更多的福音。
电子商城
服务
Ignion可支持多协议、宽频段的物联网天线方案设计,协议:Wi-Fi、Bluetooth、UWB、Lora、Zigbee、2G、3G、4G、5G、CBRS、GNSS、GSM、LTE-M、NB-IoT等,频段范围:400MHz~10600MHz。
最小起订量: 2500 提交需求>


































































































































































































登录 | 立即注册
提交评论