How Wear Leveling Increases SSD Lifetime?




NAND flash cells are arranged in pages and blocks. Data is written on pages, but the minimum unit of erasing is by blocks. Due to the nature of flash, the cells wear out with each program and erase (P/E) cycle, rendering the flash storage usable for a finite period of time.
In the past, the life expectancy of flash was largely dependent on its type. Single-level cell (SLC), which stores only one bit per cell, was deemed the most reliable and longest enduring. Multi-level cell (MLC), which stores two bits per cell, was rated next to SLC. Triple- and quad-level cell TLC/QLC were rated for consumer use only and were not considered fit for the demands of enterprise and industrial applications due to their low endurance.
Thanks to big strides in technology, flash storage has come a long way largely due to powerful flash controllers that enable greater reliability and longer usable product life.
In this article, we discuss one of the most common flash controller functions that help maximize the life expectancy of flash storage.
Wear Leveling
Wear leveling mechanisms allow the flash storage device to evenly distribute the P/E cycles among all blocks. It prevents the premature wearout of overused blocks, so all blocks can be used to the maximum. Wear leveling extends the life span and improves the reliability and durability of the storage device.
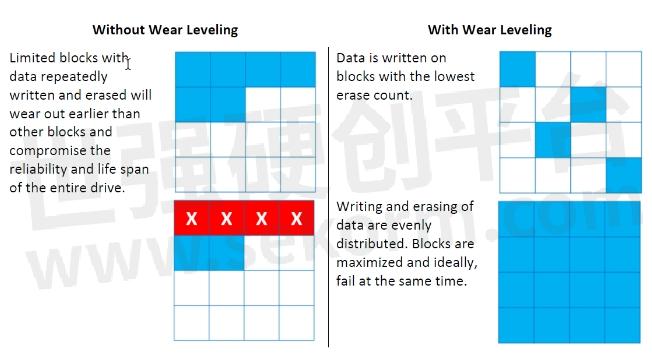
Figure 1. A graphical representation of a storage device with and without wear leveling.
There are three types of wear leveling:
Dynamic. Makes sure that data is written only on blocks with the lowest erase count. The downside is that wear leveling is limited only to “hot” or frequently modified areas, so blocks that hold rarely accessed, static data are not included in the pool of free space, thus limiting the number of blocks going through wear leveling.
Static – Includes static data or “cold” blocks in the wear leveling process. If a block contains static or rarely accessed data, its write/erase count is low. The data is moved from “cold” blocks to “hot” blocks and the freed-up block is added to the pool of free space for future use. Reassigning static data is a more complex process because it involves multiple operations to move static data around. While more effective at extending flash storage life span, static wear leveling only covers a single flash die.
Global – Works like static wear leveling by including both free space and blocks with static data, but the main difference is that its coverage extends to the entire flash storage device.
The following figure illustrates the differences in executed areas:
Dynamic Wear Leveling
Single die
Free Blocks only
Static Wear Leveling
Single die
Free Blocks + User Data Blocks
Global Wear Leveling
Multiple dies, entire device
Free Blocks + User Data Blocks
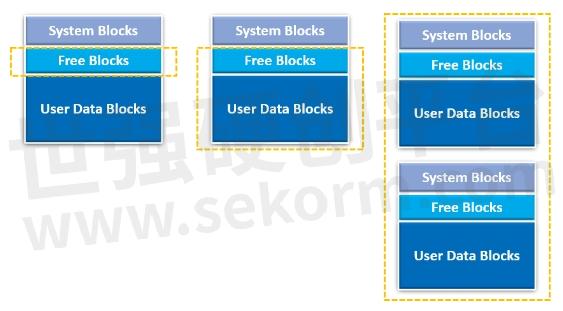
Figure 2. Differences in executed areas for Dynamic, Static and Global Wear Leveling. Image Reference: Embedded Computing
ATP Enhanced Wear Leveling
ATP implements global wear leveling on its flash memory products, using an advanced algorithm that carries out both dynamic and static wear leveling to ensure that the flash product is used to the fullest extent of its life span.
ATP Enhanced Wear Leveling treats and manages all NAND flash components in ONE drive as a unified memory management unit. The wear leveling is carried out by the flash controller and is independent of the host system, thus minimizing impact on system performance.
How it works:
There are four main steps for the “enhanced wear leveling” mechanism:
Establish and update the link table, which is used to convert the host’s logical address to the flash memory’s physical address.
Record the “erase counts” of all the blocks in one zone and save them to the wear leveling table. The table is maintained by a RAM register unit in the controller. The table will keep every block’s “erase count” within the flash memory ICs.
Find the static block (with “0” erase count) and save this block address in the wear leveling pointer. The pointer is used to select the next available block to be swapped.
Check the “erase count” when a block is taken out from the spare pool. If an over-count block is bigger than the spare block, swap the static spare block with over-count block. “Over-count” means that the block’s erase count is already higher than the Wear Count Register, and this block should be swapped as soon as possible.
Conclusion
Wear leveling is needed to address the finite program/erase capability of NAND flash memory cells. When only a limited number of blocks are repeatedly used, the device can prematurely wear out. By even distributing the program/erase cycles over the entire flash storage device, the ATP Enhanced Wear Leveling mechanism makes sure that all memory cells are used to the maximum, thereby extending the life span of the device.
- |
- +1 赞 0
- 收藏
- 评论 0
本文由涂抹转载自ATP Blogs,原文标题为:How Wear Leveling Increases SSD Lifetime,本站所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源,不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
相关研发服务和供应服务
相关推荐
The Doctor is in: ATP PLP Diag Offers Proactive Capacitor Health Checks to Avert PLP Failures
As more industries and enterprises rely on SSDs for reliable data storage under all circumstances, especially during unpredictable power loss events, ATP Electronics strengthens its SSDs‘ MCU-based HW PLP design with PLP Diag. By proactively monitoring the health of its polymer tantalum capacitors and responding to potential failures that expose the in-flight data to risks, PLP Diag offers fail-safe protection to ensure uncompromised data integrity and device reliability.
What is Error Detection Correction, LDPC, BCH, Reed-Solomon Algorithm?
As NAND flash lithography scales down, cell geometries shrink and cells store more bits per cell, densities increase but so do error bits. To ensure the reliability of its industrial flash storage products, ATP employs advanced error detection and correction technologies.
SSD Endurance: Challenges and Solutions
In this article, we will look at some factors affecting SSD life expectancy and how these can be addressed to manage SSD endurance.
PCIe®Gen 3 NVMe M.2 2280/2242/2230 SSD专业存储和内存解决方案的全球领导者
描述- ATP推出PCIe Gen 3 NVMe M.2 SSD,具备数据保护、加密和散热解决方案。产品支持多种容量和温度范围,提供高性能和可靠性,适用于嵌入式和工业应用。
型号- FT960GP38AG8BPC,N750PI,FT480GP38ANDBFC,FT120GP38AG8BPC,FT480GP38AG8BPC,FT480GP34ANDBFC,FT960GP38AG8BPI,FT240GP38AG8BPC,FT120GP38ANDBFC,N700PC,FT240GP38AG8BPI,FT120GP38AG8BPI,N600SC,N650SI,N600VI,FT960GP34ANDBFC,N700PI,FT240GP38ANDBFC,N600SI,FT120GP34ANDBFC,N650SC,FT240GP34ANDBFC,N600VC,FT480GP38AG8BPI
笔记本需要更换大容量硬盘,求推荐性价比更的SSD固态硬盘。
您好,推荐ATP(华腾国际)的SSD固态硬盘,M.2 NVMe接口最高容量可达1TB,M.2 2280接口最高容量1TB,SATA接口最高容量1TB,具体可参考【选型】ATP(华腾国际)内存及存储产品选型指南
ATP对所有SSD进行数千小时RDT测试,确保产品严格遵守最高质量标准
可靠性验证试验(RDT)是对ATP固态驱动器(SSD)进行的一项长期严格测试,旨在证明每个SSD符合最严格的质量要求。ATP在较长时间内对其 SSD执行完整的实际驱动器级别测试,以验证额定MTBF值,而不是依赖可靠性预测系统。
ATP NVMe BGA pSLC SSD安全保护及加密功能特点
硬件写保护* 写保护功能将ATP NVMe BGA SSD置于“只读”模式,以防止数据写入设备,并保护重要数据不被意外删除、移动或修改。通过在控制器印电路板(PCB)上的通用输入/输出(GPIO)信号引脚的特定引脚上放置跳线,在存储设备上启用写保护。硬件快速擦除*对于特定应用,主机可以使用GPIO连接器触发“擦除数据”行动。
ATP AcuCurrent: Innovative Signal Integrity Optimization Technology
ATP‘s AcuCurrent Technology is an innovative signal optimization technology, enabling dynamic, real-time temperature-responsive drive setting adjustments across a wide operating range, up to 125℃. AcuCurrent Technology is temperature-responsive, dynamically adjusting settings in real time to ensure that the SSD operates at great efficiency across various scenarios, effectively minimizing unnecessary read-retry cycles, and substantially reducing error rates.
ATP推出工业宽温企业级SSD系列产品N651Sie,包含U.2,M.2,E1.S三种接口类型
ATP推出工业宽温企业级SSD系列产品N651Sie,结合了工业级固态硬盘和企业解决方案的优点,专为在不受控制的恶劣环境中处理企业级工作负载而设计。
【经验】什么是SSD的M.2标准?M.2 SSD和mSATA SSD之间又具体有哪些差异?
近年来发布的固态驱动器(SSD)变得更快,并且能够处理大量数据。但是,它们的全部功能受到与其连接的接口的阻碍或限制。Mini-SATA(mSATA)接口虽然专为提供最小的SSD尺寸而设计,但受到SATA 6 Gb / s的限制。M.2标准是内部安装的计算机附加卡的规范,旨在解决mSATA的局限性,并为小型卡(包括不同大小和容量的SSD)提供更多选择。
PCIe®Gen 3 NVMe M.2 2280/2242/2230固态硬盘
描述- ATP推出的PCIe Gen 3 NVMe M.2 2280/2242/2230 SSD,基于NVMe协议和PCIe Gen3 x4接口,提供高速、可靠和持久的性能,满足嵌入式和工业应用日益增长的数据存储需求。这些模块采用3D TLC NAND闪存,容量从40GB到960GB不等,适用于不同的数据存储需求。
型号- FT960GP38AG8BPC,N750PI,FT480GP38ANDBFC,FT120GP38AG8BPC,FT480GP38AG8BPC,FT480GP34ANDBFC,FT960GP38AG8BPI,FT240GP38AG8BPC,FT120GP38ANDBFC,N700PC,FT240GP38AG8BPI,FT120GP38AG8BPI,N600SC,N650SI,N600VI,FT960GP34ANDBFC,N700PI,FT240GP38ANDBFC,N600SI,FT120GP34ANDBFC,N650SC,FT240GP34ANDBFC,N600VC,FT480GP38AG8BPI
ATP推出业界最高擦写寿命的工业级固态硬盘(SSD),具有出色的耐久性和在极端温度下工作的能力
ATP推出N751Pi系列PCIe Gen4 NVMe M.2 2280 SSD,该SSD在配置了pSLC NAND的工业级固态硬盘(SSD)中具有出色的耐久性和在极端温度下工作的能力,是恶劣环境、恶劣条件和高负荷工作负载下关键任务和写入密集型应用的理想选择。
ATP‘s Power Loss Protection Just Got Smarter with MCU-based SSD Design
ATP customers want constant assurance that power loss events will not cause massive downtime or lost data that could affect business operations and lead to higher operating costs. The MCU intelligently monitors sudden power failure conditions from a glitch to a surge or a complete outage...
ATP Industrial Enterprise SSD Series: The Best of Both Worlds, Engineered for Uncontrolled Environments at the Edge
ATP offers the best of both of industrial and enterprise worlds: THE NEW INDUSTRIAL ENTERPRISE Series, which leverage NVMe PCIe Gen4x 4 and are available as M.2, U.2, and E1.S. They combine the best of enterprise and industrial features, making them excellent as boot drives, data storage drives, or mixed-use drives.
【产品】ATP的SSD固态存储盘,具有静态数据安全功能,可快速安全地删除所有数据
ATP的SSD固态存储盘,具有静态数据安全功能,可快速安全地删除所有数据,可应要求提供各种客户和应用程序特定功能,以防止未经授权访问SSD,系统或网络,定义读/写访问限制(包括WORM)或验证要访问的内容。
电子商城
现货市场
服务
可烧录MCU/MPU,EPROM,EEPROM,FLASH,Nand Flash, PLD/CPLD,SD Card,TF Card, CF Card,eMMC Card,eMMC,MoviNand, OneNand等各类型IC,IC封装:DIP/SDIP/SOP/MSOP/QSOP/SSOP/TSOP/TSSOP/PLCC/QFP/QFN/MLP/MLF/BGA/CSP/SOT/DFN.
最小起订量: 1 提交需求>
拥有IC烧录机20余款,100余台设备,可以烧录各种封装的IC;可烧录MCU、FLASH、EMMC、NAND FLASH、EPROM等各类型芯片,支持WIFI/BT模组PCBA烧录、测试。
最小起订量: 1 提交需求>









































































































































































































登录 | 立即注册
提交评论