Selecting the Right Resistor for High-Temperature Apps




Until recently, the limiting factor in high-temperature electronics has been the degradation in semiconductor properties of the active components used. However, with recent advances in high-temperature semiconductors and silicon-carbide-based materials, passive components such as resistors have been the limiting factor. As a result, proper resistor selection has become a critical factor in the design of high-temperature electronics to ensure proper operation and reliability.
Resistors have traditionally been manufactured by a variety of methods and technologies, including metal and metal-oxide film, metal foil, carbon, wirewound, and thick-film methods. Each has specific characteristics that make them more or less suitable for high-temperature applications. Resistor degradation at high temperature can vary from a small resistance change over time to a catastrophic change in resistance, exhibited by either becoming open circuit or, in some cases, a short circuit.
Although thought of as a mature technology, many wirewound resistors actually fare quite well in high temperature applications up to ambient temperatures of 200 to 250°C and above. Of relatively simple construction, wirewound resistors are made by winding a resistance wire (such as Nichrome, which has very good high-temperature characteristics and is often used in heating elements), onto an alumina or steatite ceramic core, and welded to metal end caps press-fit onto each end.
The resistor is typically insulated and made weatherproof by encapsulating the unit using a vitreous enamel (glass), silicone, cement, or epoxy compound. The encapsulation material is often the “weakest link” and can be the source of failure at high temperatures. This can be the result of a difference in thermal expansion coefficient causing cracks in the coating and allowing humidity or moisture ingress, initiating stresses on the underlying wire, or due to decomposition or degradation in its insulating properties at high temperature. As a result, epoxies generally aren’t best suited for long-term high-temperature applications, but silicones and vitreous enamel materials function well.
Vitreous enamel-coated resistors create a near hermetic package and provides additional protection in hazardous environments that occasionally can be associated with high operating temperatures, especially in the oil and gas industry. One caveat, though, is that the bulk resistivity of the enamel-coating material tends to drop significantly at high temperatures, and it’s been known to affect the overall installed resistance as the insulation properties are significantly reduced with increasing temperature.
The high temperature stability of vitreous enamel-coated wirewound resistors is quite good, exhibiting resistance changes of around 1-2% upon exposure to 200°C for 1000 hours, with typically larger changes for other wirewound resistor types. One downside to wirewound resistors is their limited upper resistance range, inherent associated inductance (although this can be greatly reduced by specifying a non-inductive “Ayrton Perry” winding, which essentially winds two wires in opposite directions around the core to cancel inductance), and their relatively large size. As a result, other resistor types hold more promise for high-temperature operation.
Thick-film resistors have received a significant amount of attention for high-temperature applications in recent years. These resistors are made by depositing a blend of metal and particles onto a ceramic substrate and firing at a high temperature (typically 850°C or so in air) which creates a conductive cermet matrix. Thick-film conductor formulations for high temperature use are typically gold, palladium-silver, or platinum-silver (Fig. 1). After laser trimming to value, a layer of glass insulator is often applied on top for environmental protection. Thick-film resistors can be made quite small, routinely down to 0201 or smaller in surface-mounted sizes.

1. Shown is thick-film chip resistor construction.
Because the initial processing temperature for thick-film resistors is quite high, this technology holds excellent promise for future developments of high-temperature applications. Testing of special high-temperature thick-film resistors manufactured by TT Electronics show less than 0.25% average resistance change after 1000 hours (no load) at 300°C (Fig. 2).
2. The effects of high-temp exposure are demonstrated by 1000-hr no-load resistance change (HTC series, 0805 size, 180 kΩ, 20 pcs).
For operation at high temperatures, traditional solders aren’t an option (typical lead-free solders have a liquidus temperature of approximately 221°C), so other methods of attachment including wirebonding, high-lead-content HMP solder (often Sn05Pb93.5Ag1.5-296°C), or conductive adhesives are used. As a result, it’s necessary to select the termination materials compatible with the attachment method. This usually requires gold terminations for wirebonding or conductive adhesives, polymer silver, Pd-Ag or Pt-Ag for conductive adhesives, and plated materials with a nickel underlayer for HMP solders.
For thick-film resistors, the typical temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) is approximately ±100 ppm/°C over normal temperature ranges, but it can be (and often is) dramatically nonlinear as the temperature deviates from normal ranges (Fig. 3). However, even if we assume a TCR of 100 ppm/°C, operation at 200°C above ambient can result in a perceived resistance change of as much as 2% simply due to the temperature excursion—and possibly much more depending on the actual TCR characteristics at higher temperatures. As a result, more precise applications may require thin-film networks or wirewound resistors.
3. Typical TCR characteristics of thick-film resistors.
Unlike thick-film resistors, which are characterized by an additive high-temperature manufacturing process, thin-film resistors are typically manufactured using a subtractive, sputter deposition process. Subsequent manufacturing operations are used to condition the resistor films to optimize high-temperature performance. Thin-film resistors are typically characterized by low TCR, precision performance, and often available in networks or packages with more than a single resistor.
The thin-film resistor material of choice is typically either a nichrome alloy or tantalum nitride. Both of these materials (see table) tolerate high melting points, which tend to result in less microscopic grain growth at high temperature and are highly resistant to oxidation—two potential sources for significant resistance change at high operating temperatures.
The table illustrates characteristics of common thin-film resistor materials.
Both resistor films offer good resistance stability and excellent low TCR at normal operating temperatures which carry over to some extent at high temperature operation. In addition, they both possess a relatively linear TCR curve over a wide temperature range (Fig. 4). Although the data shown is for a nichrome-alloy metal film resistor, similar characteristics are seen with the tantalum-nitride materials. An additional benefit is illustrated in the graph, which demonstrates the close TCR tracking or matching between the resistors in the common network (in this case, a 7-resistor network).
4. The TCR of thin-film resistors in a DIP network is shown at elevated temperature.
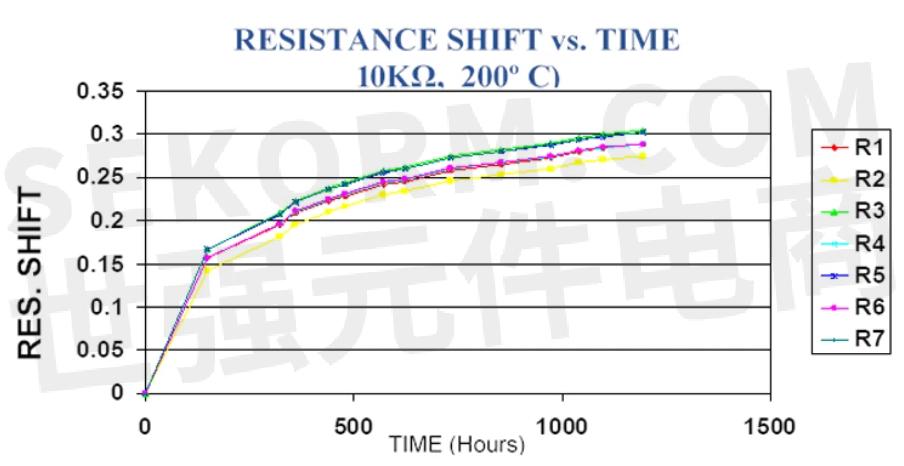
One intriguing aspect of thin-film resistors is that a significant amount of the total resistance change occurs during the first 100 to 200 hours of operation (Fig. 5). Various mechanisms, such as oxidation, migration of metallic layers, or metallic diffusion can cause this resistance change.
5. The thin-film resistance shift with time at elevated temperature reveals that a significant amount of total resistance change occurs during the first 100 to 200 hours of operation.
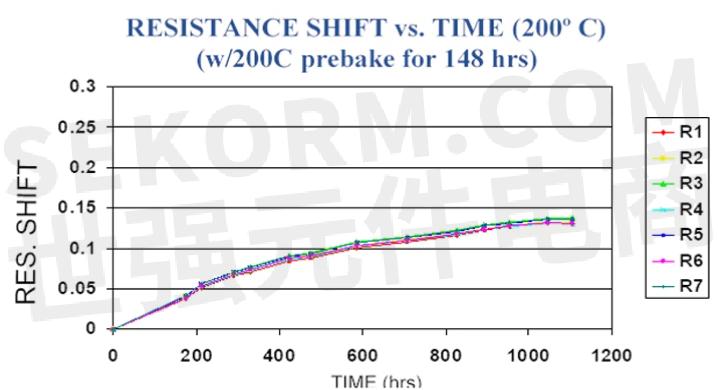
However, the rate of resistance change significantly decreases over time, which allows for a marked reduction in the absolute change in resistance over life by subjecting the resistors to a high-temperature bake at or exceeding the temperature that the resistors will be used. This reduction in the resistance change is illustrated in Figure 6, showing a similar resistor network as in Figure 5, but with a 200°C, 148-hr bake added. In this case, the resistance change has been reduced to less than half over 1,000 hours of exposure, dramatically improving overall resistor stability.
6. This resistor network is similar to that as in Figure 5, but with a 200°C, 148-hr bake added. The image depicts a reduction in the resistance change, reduced to less than half over 1,000 hours of exposure, significantly improving overall resistor stability.
Figure 6 also demonstrates another important characteristic: All of the resistors in the common network track each other very well over time and temperature. This makes it possible for very accurate resistor divider and voltage ratio networks to provide excellent performance, even at elevated temperatures.
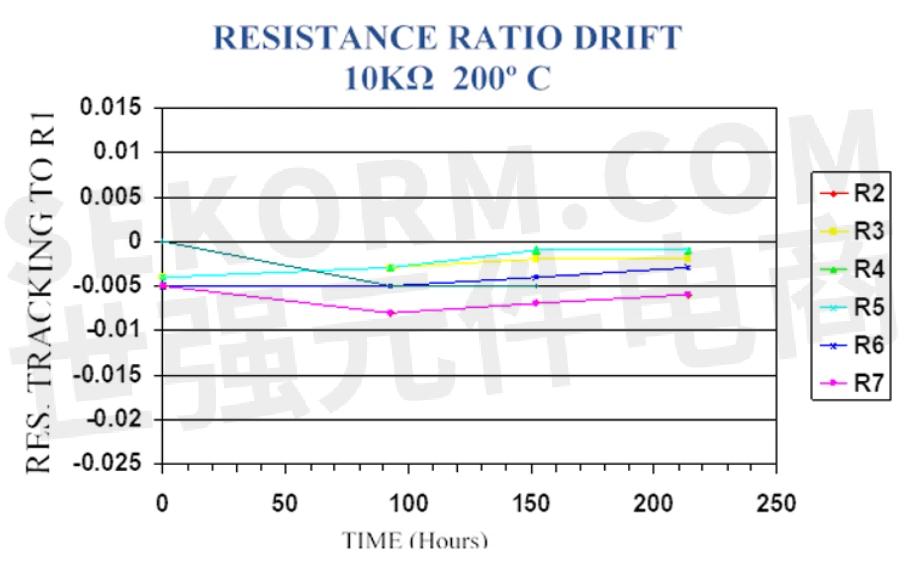
It almost always lowers cost to specify a resistor network with two or more resistors (of different values) that track each other well, rather than using individual resistors that will give similar tracking and matching performance. Figure 7 illustrates the typical ratio tolerance performance of a high temperature resistor network—the difference in ratio performance is within 0.005% (50 ppm) over life.
7. The plot illustrates the ratio drift between resistors in a high-temperature resistor network.
Thin-film resistor networks can be purchased in a variety of package configurations, such as SOT23, SOT147, SOIC, QSOP, BGA in SMT, along with the mature through-hole packages like SIP/DIP configurations. The 3-terminal (2-resistor) 1206 divider package shown in Figure 8 offers outstanding high-temperature performance and excellent resistor tracking over time and temperature. Both gold and solder terminations allow flexibility in attachment.
8. Shown is a cost-effective, 1206-size, high-temperature divider package (PFC-HT Series).
Other Resistor Types
A variety of other resistor types are available to the design engineer. These include composition, foil, metal oxide, and others. With the exception of foil technology, other resistor types generally suffer from reduced performance in high-temperature applications and have limited applicability. Foil resistors usually exhibit very good performance, but they come at a very high cost. Very low resistance value resistors (such as for shunts or current-sensing applications) can be facilitated in high-temperature applications by using metal-strip or formed-metal resistors.
Conclusion
Proper selection of resistors for high-temperature applications is critical for optimum performance and economy. Although many resistor technologies are available to the circuit designer, knowledge of each type’s characteristics and construction is necessary to make the best selection.
- |
- +1 赞 0
- 收藏
- 评论 0
本文由赚钱养太阳转载自TT,原文标题为:Selecting the Right Resistor for High-Temperature Apps,本站所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源,不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
相关推荐
TT Electronics (TT)电阻器选型指南
目录- Technology and Product Selector Guides Current Sense Resistors High Value/Voltage Resistors Surge/Pulse Resistors High Power Resistors Precision/Fusible Resistors High Reliability Resistors Temperature Sense & Thermal Management Resistors Zero-Ohm Jumper & General Purpose Resistors Colour Code for Band-marked Resistors
型号- BCN168SB,WH SERIES,T 2010,WP25S,WMO7S,BCN168RB,0612X,BCN,WP5SZI,WHS-UL,WIN SERIES,RCP,SQM5,SQM3,SQM2,EBW5216,N 0815,LRF SERIES,SQM7,4507,LRCS,4500,WMO5S,4501,4502,4503,4504,VRW37,4505,4506,RHVD08,RC70P,T0603,WRM SERIES,HDSC,CR,LVC SERIES,VRW25,DIV23 SERIES,ULW SERIES,RHVD15,LRMAPXXXX SERIES,4530,GHVC SERIES,ULR3N,4531,WDBR-UL,TJC,RHVD10,RC65,WMO3S,BPR50,WH10,ULR,EMC,LCS SERIES,ULW,WP-SZI SERIES,WHPC,PCF,WMO2S,RC55,4532,4533,4534,4535,4536,4537,PCR,HPDC SERIES,OAR,SQP SERIES,WPYP10,ULR1S,BCN10,WSHR,ULR25,WRM,1900 SERIES,W20,WMO1S,W22,W21,T0805,W24,W23,SQP7,SQP5,ULR2N,BPR30,SQP2,SQP3,SOT143 SERIES,RC70,LR SERIES,WSM,HVC,W31,W30,HVD,WHS2,WHS3,WHS5,W20 SERIES,WH25,WHS7,WP3SZI,BPC3,RC65P,HVP,WH50,LHVC,HR,PFC,WMO-S SERIES,VRW,MFP1,MFP2,BPR10,WA84F,EBW SERIES,MF-S,WP-SZI,BPC7,BPC5,HVP SERIES,MFC SERIES,WSM2,WSMHP,WSM3,GHVC2512,MF1/2S,WCM SERIES,BPC10,LOB-5,ULR15S,LOB-3,MFR5,LRF3W SERIES,MFR3,MFR4,HVD08,RHVD10A,WH100,RC SERIES,VRW SERIES,SOT,RC55P,WSMHP25,HVD15,LR,WSMHP20,HVD12,1020X,DIV23,SPP,WMHP35,DSC,0508X,WRM-HP SERIES,WP-S SERIES,MF2S,LOB SERIES,MFR SERIES,HVD20,WHS10,WH200,WMHP50,SQM,PFC-HT,LRZ SERIES,SQP,BPC,LRMA,WSMHP SERIES,OARS-XP SERIES,LCS,MF1S,EMC SERIES,PR SERIES,BPR,WMHP20,N 0612,MFC,HVD30,RHVD15A,PCFH,T43,OARS-XP,T44,MFP,MFR,PCFP,T48,WCR SERIES,WA84F SERIES,WSMHP35,4530 SERIES,WH300,T0402,APC,HPWC,MF3S,VRW68,PR,WPYP SERIES,LRCS SERIES,OAR-5,OAR-1,OAR-3,1908,RC,PCR SERIES,RHVD SERIES,PCF SERIES,WHS5UL,1906,1905,1900,N 1225,BCN SERIES,PWC SERIES,1600 SERIES,LRF3W,ASC,WHPC SERIES,MFP SERIES,HTCR,PWP08,RCP SERIES,CAR SERIES,APC SERIES,WPYP8,P4026,PR5,PR4,TJC SERIES,WMHP,WP-S,SQM SERIES,SPP SERIES,PWP04,PWP06,OARS1,GHVC1206,T1206,OARS SERIES,HVP08,HVP06,TFHP SERIES,HVP04,WHS-UL SERIES,WRM-HV SERIES,PTS SERIES,HVD SERIES,M 2512,WSM SERIES,P 3920,WMO1/2S,WHS SERIES,SC3 SERIES,HVP15,ULR SERIES,HVP10,SPP-1,T 2512,LHVC SERIES,SPP-3,PTS,SPP-2,ULR2,ULR1,WH,WP2S,BPR SERIES,EMC2,WDBR1/2,ULR5,TFHP,HVP20,ULR3,M 1206,WL4 SERIES,BPR7,0207HP,BPR5,1602,BPR3,1601,SP20F SERIES,1600,WP1S,WPRT,WRM-HV,GCR,1609,1608,1607,1606,1605,SP20F,1604,1603,WRM-HP,WCM,WMHP SERIES,WCR,BPC SERIES,PFC-D,BCN164A,WP4S,WDBR5,WDBR SERIE,WDBR7,WDBR2,CAR7,PWC,WDBR1,CAR6,LOB,CAR5,WDBR3,PWP,P 2512,WP3S,BCN164AB,WPRT10,WPRT15,M 0805,P2817,OARSXP,RHVD,P 2726,WMO-S,WPRT20,EBW,3810,3811,WP2SZI,3812,CR SERIES,S0M10,DSC SERIES,WMHP100,GHVC,4800 SERIES,WPRT30,WP5S,HTCR SERIES,LRF,WH5,LRMA SERIES,P 5930,4804,4805,WPRT40,LRZ,GHVC2010,GCR SERIES,WPYP,PWP10,4800,PWP15,4802,WHS,HPDC,EBW8518,MF-S SERIES,OAR SERIES,PWP SERIES,4500 SERIES,ULW5,ULW4,ULW3,ASC SERIES,WPRT50,CAR,ULW2,OARS,PWP20,WHS3UL,W30 SERIES,4812,WIN,SQP20,SQM10A,LRMAPXXXX,3810 SERIES,WPRT SERIES,SOT143,HR SERIES,HVC SERIES,SQP15,SC3,SQP10,WDBR,WHS2UL,LVC,PFC-D SERIES,4832,WL4
【产品】有三种封装尺寸的高温厚膜片式电阻,200℃高温仍能工作
HTC系列是TT Electronics集团推出的一系列高温厚膜片式电阻,可在高温至200℃的条件下工作,堪称是优异的高温稳定性。HTC系列高温厚膜片式电阻采用无铅环绕终端,且所有产品均符合RoHS标准,可应用于电路保护,电路检测,电源管理和信号调理等领域。
客户欧盟REACH、英国REACH和JS709C声明
描述- TT Electronics-IRC致力于遵守欧盟和英国REACH法规以及低卤素法规的要求,并与供应商合作监控化学物质、制剂和文章对产品的影响。其电阻产品不属于“有意释放”的物品类别,因此无需向客户提供额外文件,目前预计不会对产品供应造成中断。所有标准无铅固定电阻产品和相关包装材料均不含有REACH法规候选清单中的SVHC物质,或附件XIV或附件XVII中列出的物质,以及英国REACH法规的相应清单和附件中的物质,除非附录A中列出的产品含有>0.1%w/w的铅,符合RoHS豁免条件。所有标准固定电阻产品均符合JS709C对低卤素产品的要求。详情请参考网站上的合规标签。
型号- GUB,HTC
产品数据简表电阻器BI Technologies IRC Welwyn
描述- 该资料由TT Electronics plc提供,介绍了其电阻器产品线。内容包括不同类型的电阻器技术、产品系列和应用案例。重点强调了公司在医疗、航空航天和消费电子产品中的应用解决方案。
型号- BCN168SB,WH SERIES,OAR-5,1210,WP25S,T 2010,WMO7S,0805,OAR-1,OAR-3,WLT,1218,BCN168RB,1908,BCN,PLO-5,WP5SZI,PLO-3,1225,PLO-7,W215,1906,1905,RCP,1900,SQM5,SQM3,SQM2,N 1225,N 0815,SQM7,4507,ASC,LRF3W,CC SERIES,PFCHT,LRCS,WP-S,4500,WMO5S,HTCR,4501,4502,4503,4504,GC55,VRW37,4505,4506,RHVD08,PWP08,RC70P,WPYP8,MFR4P,T0603,PR5,PR4,1005,WMHP,VRW25,PWP04,PWP06,RHVD15,4530,OARS1,4531,CHP,1020,T1206,PLO-10,RHVD10,GC70,HVP08,HVP06,RC65,WMO3S,HVP04,BPR50,WH10,EMC,ULR,0603,ULW,PWRL,M 2512,P 3920,WMO1/2S,WHPC,PCA,0612,PCF,WMO2S,RC55,4532,HVP15,4533,SQM10,4534,GC65,4535,4536,BCN4D,4537,PCR,HVP10,SPP-1,OAR,T 2512,WPYP10,2010,ULR1S,BCN10,PTS,SPP-3,ULR25,SPP-2,ULR2,ULR1,WP2S,WRM,W20,WMO1S,W22,W21,EMC2,T0805,W24,WDBR1/2,WBC,W23,HVP20,0503,ULR3,SQP7,SQP5,M 1206,BPR30,SQP2,SQP3,BPR7,RC70,BCN21,BPR5,WSM,1602,BPR3,1601,1600,WPRT,WP1S,HVC,W31,W30,WRM-HV,GCR,HVD,WHS2,WHS3,1609,1608,WHS5,1607,2817,1606,WH25,SP20F,WHS7,1605,WP3SZI,1604,WRM-HP,1603,BPC3,RC65P,HVP,WH50,WCR,LHVC,PFC,PFC-D,BCN164A,WP4S,0402,WDBR5,BCN318SB,WDBR7,PCA164,CHP2,CHP1/2,CHP1,VRW,MH37,WDBR2,CAR7,WDBR1,CAR6,LOB,MFP1,CAR5,CHP1/8,MFP2,WDBR3,BPR10,WA84F,P 2512,GPCF,WP3S,BCN164AB,WPRT10,MH25,MF-S,WP-SZI,WPRT15,PWC,BPC7,M 0805,1505,MAR,BPC5,RHVD,OARSXP,PWP,WSM1,WSMHP,WSM2,WSM3,GC SERIES,MF1/2S,LOB-1,0303,WMO-S,BPC10,LOB-5,ULR15S,PTCR,LOB-3,MFR5,WPRT20,3810,3811,WP2SZI,MFR3,3812,CR SERIES,MFR4,HVD08,RHVD10A,WH100,WMHP100,RC SERIES,SPP,LR (F),BCN318RB,SOT,WPRT30,RC55P,WP5S,MAR 40,WSMHP25,HVD15,WH5,WSMHP20,HVD12,4804,0204,4805,DIV23,0202,WMHP35,WPRT40,DSC,LRZ,0201,WPYP,PWP10,MH,4800,PWP15,MF2S,4802,0207,WHS,HVD20,WHS10,WH200,WMHP50,SQM,PFC-HT,ULW5,SQP,ULW4,2512,BPC,ULW3,CAR,WPRT50,ULW2,OARS,PWP20,LRMA,LCS,WIN,4812,MAR 42,MF1S,CRT,PR SERIES,BPR,SQP20,WMHP20,N 0612,MFC,HVD30,RHVD15A,PCFH,CC1,LR(F),PLO,T43,OARS-XP,CC2,T44,0102,MFP,MFR,PCFP,T48,SOT143,HR SERIES,SQP15,SC3,WSMHP35,SQP10,WH300,1206,T SERIES,HPWC,WDBR,LVC,4832,MF3S,WL4,VRW68
EOL公告-RB系列绕线电阻器(PCN-2021-RBU02)
描述- TT Electronics宣布RB系列玻璃釉绕线电阻器即将停产。受影响的零件编号和推荐替代品可在附录1中找到。由于销量和需求下降,该产品不再具有经济可行性。建议客户订购W20系列等效电阻器。
型号- W21-33RJPB,W22-120RJI,W21-33RJI,RB59-2K2JI,RB59-150RJI,W21-R33JI,W21-R10JI,RB57-4K7JI,W22-22RJI,W21-3R3JI,RB57-4R7JI,W22-10KJI,W21-4K3JI,RB59-1K2JI,RB59-1K0JI,RB SERIES,RB59-7R5JI,W21-R22JI,RB59-820RJI,W21-R20JI,RB59-R27JI,W22-470RJPB,W21-1K2JI,W22-4K7JI,RB59-47RJI,W21-2K2JI,W22-680RJI,RB57-10KJI,RB59-33RJI,RB59-R10JI,RB59-R33JI,RB57-2K2JI,RB59-33RJPB,RB59-3R3JI,W21-1K0JI,RB59-4K3JI,W21-150RJI,W22-2K2JI,W22-4R7JI,RB59-R20JI,W21-7R5JI,RB59-R22JI,W21-R27JI,RB57-120RJI,RB57-22RJI,RB57-680RJI,W21-47RJI,W20 SERIES,W21-820RJI,RB57-470RJPB
WA80Z系列水泥涂层表面安装绕线电阻器数据表
描述- 本资料介绍了Welwyn Components生产的WA80Z系列陶瓷涂层表面贴装绕线电阻器。这些电阻器采用全焊接结构,适用于自动拾取和放置设备,具有优异的脉冲处理能力,在故障条件下安全熔断,且价格竞争力强。
型号- WA80Z,WA80Z SERIES,WA84Z1K5J,WA85Z,WA84Z,WA83Z
线绕电阻器的脉冲和过载能力.应用说明
描述- 本资料详细介绍了TT Electronics生产的线绕电阻在脉冲处理和过载特性方面的应用。内容包括不同类型线绕电阻的脉冲能力和过载能力数据,包括金属外壳、轴向水泥釉化和玻璃釉化线绕电阻。此外,还提供了能量容量和过载率图表,用于评估脉冲应用中的热冲击风险。资料还包括了关于重复或叠加脉冲的处理方法,以及如何计算等效脉冲能量的公式示例。最后,提到了定制设计和WHS系列高浪涌电阻产品。
型号- WH,W20,W31,WP-S,WA80
GWCR Series Green Thick-Film Chip Resistors
描述- 该资料介绍了TT Electronics公司生产的GWCR系列绿膜贴片电阻器的详细信息。这些电阻器符合欧盟RoHS2指令,无铅且环保。资料涵盖了产品的尺寸、功率等级、阻值范围、温度系数、耐压、绝缘电阻等电气数据,以及物理尺寸、重量、构造、可焊性、强度等物理数据。此外,还提供了产品的标记方式、溶剂抵抗性、性能数据和包装信息。
型号- GWCR0201,GWCR2512,GWCR0402,GWCR1206,GWCR1812,GWCR0603,GWCR1206-10KFT5,GWCR0805,GWCR2010,GWCR,GWCR01005,GWCR1210
GWCR系列绿色厚膜片式电阻器规格书
描述- 本资料介绍了TT Electronics公司生产的GWCR系列绿色厚膜芯片电阻。该系列产品完全不含铅及其化合物,符合欧盟RoHS指令2011/65/EU修订版(RoHS3)。产品尺寸从01005到2512不等,阻值范围在1R0至10M之间。资料提供了详细的电气数据、物理数据和性能数据。
型号- GWCR SERIES,GWCR1206-10KFT5,GWCR
HTC系列高温厚膜片式电阻器规格书
描述- 本资料介绍了TT Electronics公司生产的HTC系列高温厚膜芯片电阻。该系列产品适用于高达200°C的工作温度,具有优异的高温稳定性和改进的工作电压等级。产品采用无铅绕包端子设计,符合欧盟RoHS3指令要求,提供标准尺寸从1206到2512的多种选择。
型号- TKC-HTC-2512LF-100R-F,HTC,HTC SERIES
电子商城
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:High Power MELF Resistors
价格:¥0.5375
现货: 9,000
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:High Power MELF Resistors
价格:¥0.5375
现货: 9,000
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:High Power MELF Resistors
价格:¥0.3305
现货: 9,000
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:High Power MELF Resistors
价格:¥0.3305
现货: 9,000
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:High Power MELF Resistors
价格:¥0.5375
现货: 9,000
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:High Power MELF Resistors
价格:¥0.3305
现货: 9,000
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:High Power MELF Resistors
价格:¥0.5375
现货: 9,000
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:High Power MELF Resistors
价格:¥0.5375
现货: 9,000
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:High Power MELF Resistors
价格:¥0.5375
现货: 9,000
现货市场
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:Low Resistance Metal Alloy Resistors
价格:¥0.7268
现货:160,000
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:Low Resistance Metal Alloy Resistors
价格:¥0.7268
现货:107,900
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:Wirewound Power Radial Terminal Resistors
价格:¥29.9250
现货:22,389
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:Wirewound Power Radial Terminal Resistors
价格:¥7.1649
现货:814
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:Wirewound Power Radial Terminal Resistors
价格:¥16.0569
现货:42
品牌:TT Electronics
品类:Wirewound Power Radial Terminal Resistors
价格:¥17.9550
现货:7
服务
配备KEYSIGHT网络分析仪,可测量无线充电系统发射机/接收机线圈的阻抗,电感L、电阻R、电感C以及品质因数Q,仿真不同充电负载阻抗下的无线充电传输效率。支持到场/视频直播测试,资深专家全程指导。
实验室地址: 深圳 提交需求>



































































































































































































登录 | 立即注册
提交评论