Filter Basics about Different Approaches to Q Factor




To help customers with filter selection, KNOWLES generally provides a lot of information on what our filters can do. But in this new Filter Basics Series, Knowles is taking a step back to cover some background information on how filters do what they do. Regardless of the technology behind the filter, there are several key concepts that all filters share that we will dive into throughout this series. By providing this detailed fundamental filter information, we hope to help you simplify your future filtering decisions.
In part 7 of this series, Knowles performs a deep dive on the different ways you can think about the Q factor for the components going into your filter or your filter as a whole.
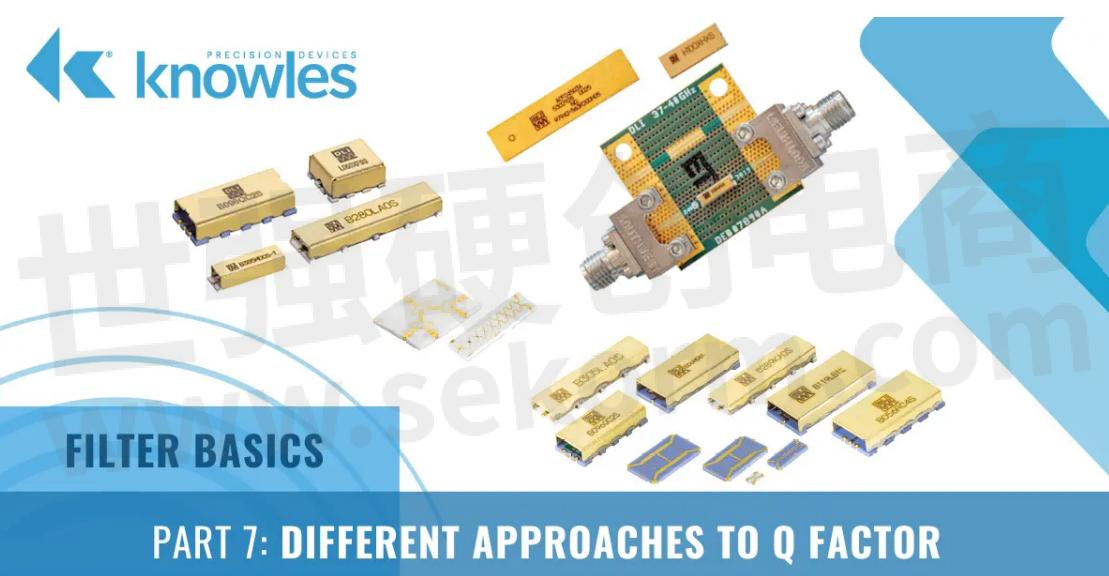
As an RF engineer, you likely frequently hear the term “quality factor”, or Q factor, used as a shorthand figure of merit (FOM) for RF filters. In short, the Q factor is expressed as the ratio of stored versus lost energy per oscillation cycle.
More specifically, the Q factor generally describes specifications such as the steepness of skirts, the selectivity, and how low the insertion loss is. Overall losses through a resonator increase as the Q factor drops and will increase more rapidly with frequency for lower values of resonator Q. However, truly understanding how the Q factor is determined is a bit more intricate. Let’s start by looking back to the example bandpass filter specification Knowles showed in Part 3.
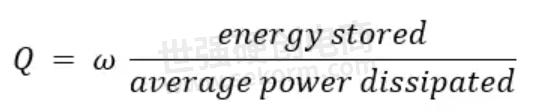

Figure 1. An example of a typical bandpass filter response.
In this example, the X axis shows the operating frequency of the bandpass filter while the Y axis shows the power allowed through the filter in decibels. Knowles can mark the following characteristics of this filter on this graph:
Center frequency – The geometric or arithmetic mean of the upper and lower cutoff frequencies or 3dB points of the bandpass filter.
Bandwidth – Usually taken from the 3dB points on either side of the center frequency.
Insertion loss – Drawn here as the loss at the center frequency. In general, when someone says high Q in reference to insertion loss, this usually means low insertion loss.
Selectivity – This is a measurement of a filter’s ability to pass or reject specific frequencies closer to the band of interest. This is what people usually mean when they talk about ‘steep skirts’ or a ‘sharp response.’ Generally, high Q means high selectivity.
Understanding the Different Components of Q Factor
There are three types of Q – loaded (QL), unloaded Q (Qu), and external Q (Qe) that make up the Q factor. QL is measured by looking at a plot of a filter’s performance. The standard definition of QL is as a FOM for bandwidth calculated with the following equation:
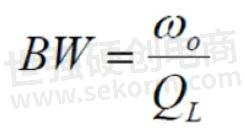
QL is driven by what goes on inside the filter, which is the Qu, and the way that the device is coupled to the external world, which is the Qe:
In general, QL is a convenient way to talk about a filter’s performance as plotted. But when it comes to what makes a filter works the way it does, it’s best to look at the QU of the resonators the filter is built up from. Now let’s look more specifically at three different ways to define the Q factor using the different types of Q.
Three Ways to Define Q Factor
As mentioned, there are actually a few different ways to define the Q factor, depending on the context of the discussion. This includes the following:
Bandpass Q Factor – This talks about the width of a filter. Sometimes this is QL , as discussed above, but with wide filters, it is tricky to use Bandpass Q Factor
Component Q Factor – Addresses individual inductor or capacitor Q
Pole Q Factor – Tells us about the performance of different parts of a filter response, and is more abstract and based on Pole Zero Plots
While component and bandpass Q are the two most common types of Q factors referenced, let’s further explore the context of all three to better understand what someone may mean when they say a filter or component has “high Q.”
Bandpass Q Factor
When connecting components to create a resonant circuit, Knowles needs to look at QL, which for bandpass filters is referring to selectivity as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2. A graph showing bandpass filter Q Factor.
If the resonant circuit has Bandpass properties, Knowles can define QL with the following formula:
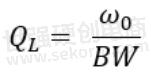
It is important to note that this approach works for narrowband filters. However, when f1 and f2 are widely separated, which usually means two octaves or more between f1 and f2, this results in a wideband with the filter often constructed by combining a high pass filter for f1 and a low pass filter for f2. In this situation, it might make sense to think about the pole quality factor instead, which we will discuss later in this post, or to look at the performance of the high pass and low pass sections and look at their QL.
Component Q Factor
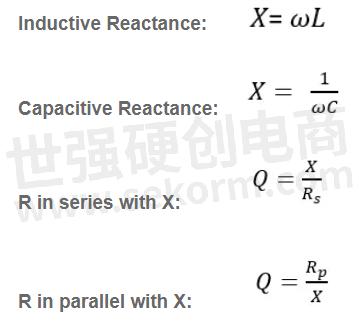
As mentioned, the component Q factor looks at just the component, such as the inductor or capacitor, in isolation from the rest of the circuit. Components have Qu related to the component values and loss. Since inductance and capacitance provide an opposition to AC that is measured in terms of reactance, let’s look at Q in terms of how the component behaves under reactance.
For a reactance with no loss:
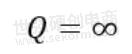
For an Inductive reactance, Q increases with frequency and decreases with loss as shown in the formula below.
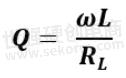
For capacitive reactance, Q decreases with frequency and with loss as shown in the formula below.
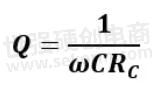
More specifically, the Q of an individual reactive component depends on the frequency at which it is evaluated, which is typically the resonant frequency of the circuit that it is used. The formula for Q depends on whether we imagine the R to be in series with or in parallel with the reactance. The following formulas can be used to calculate Qu:
Pole Q Factor
For more complex systems such as wider filters, we can look at the Pole Q factor, which tells us about the performance of different parts of the filter response. A filter has a transfer function H(s) which tells us what an output signal will look like for a given input signal.

Filter Transfer Functions are expressed in terms of the complex variable ‘s’ because some problems are much easier to solve in the Laplace domain than they are in the time domain. The output signal Y(s) can be converted back into real numbers, and we can see how a filter’s performance is determined by the structure of the transfer function H(s). We can find the values for s when the transfer function either gets large because the denominator heads to zero, or gets small because the numerator heads to zero.
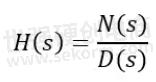
When heads to zero we call these values of s ‘zeros’ because the transfer function tends to get smaller. When heads to zero we call these values of s “poles” because the transfer function tends to get larger. In the Pole Zero Plot in Figure 3, you can see that the poles are marked with an X.
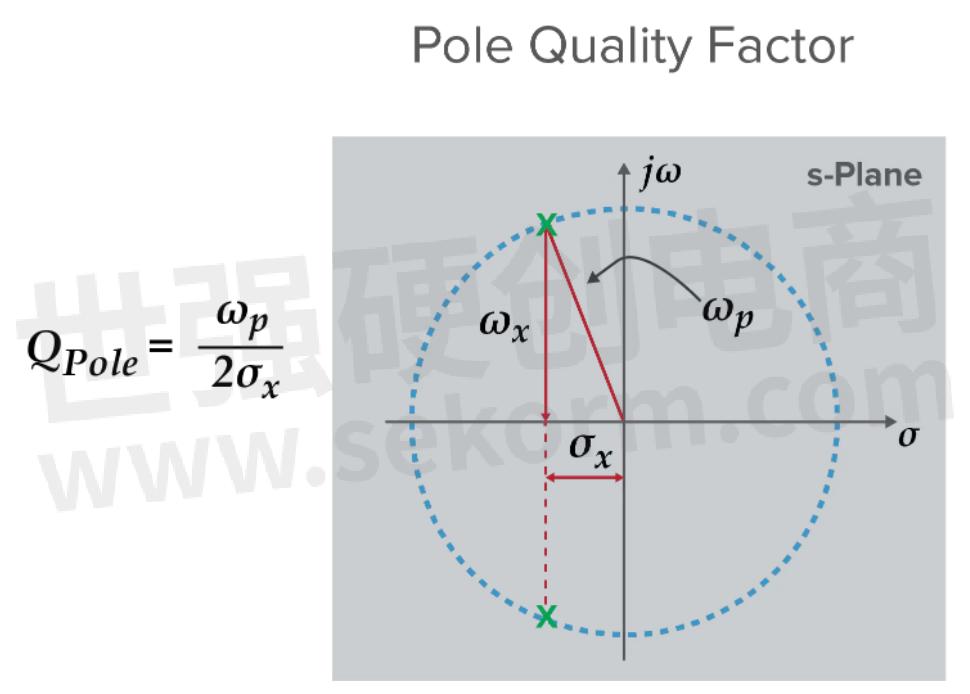
Figure 3. A Pole Zero Plot that shows Pole Q factor.
In this plot, there are two poles that are complex conjugate pairs. The length of the arrow from the origin to the X is the frequency ωp. The distance along the real axis can be written in terms of the Q factor:

Poles and zeros come from analyzing the system as a whole. Poles close to the y axis enhance amplitude response, making that part of the filter “sharp,” which is one of the ways the Q factor drives selectivity. Additionally, based on this plot, a high Q for a pole means low sigma. Since earlier we said this real component has to do with damping, which in turn is related to the energy loss of a resonator, this makes sense.
- |
- +1 赞 0
- 收藏
- 评论 0
本文由叫我大表哥吧转载自Knowles,原文标题为:Filter Basics Part 7: Different Approaches to Q Factor,本站所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源,不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
相关推荐
Knowles(楼氏电子)射频滤波器(定制产品)选型指南
目录- Company Profile Technology Capabilities Ceramic Technology Package Option Ceramic Resonators Cavity Filters Lumped Element Filters Bandpass Filters Bandreject Filters Lowpass and Highpass Dual Bands / Multi-Bands & Diplexers Multiplexers Specialty Filters Space Heritage
型号- 942274,943440,943441,943442,943443,918565,936908,940694,943480,932199,938738,936754,930257,941699,938533,935061,938576,938571,935265,934450,935264,935384,935263,942225,931406,940121,933827,936669,932342,936741,935535,935579,943503,943504,941008,942658,943627,936740,938044,942330,942331,942651,943501,943502,935838,938949,939606,936735,940989,932413,937501,938556,DR03F36Q1550AYB,933984,938635,908704,937144,936333,923787,943452,942320,942080,930615,931396,940417,937017,938663,931190,938660
Knowles(楼氏电子)微波产品选型指南
目录- Microwave Products Microstrip Filter Overview Filter Catalog Part Number Structure Bandpass Filter Lowpass Filter Highpass Filter Cavity Filters Resonators Notch Filters Custom and Build-to-Print Integrated R-C Networks Couplers Gain Equalizers mmWave Filters Speciality Kits SatCom Offerings User Guidelines:Chip and Wire or Hybrid Assembly User Guidelines:Surface Mount Recommend Reflow for Surface Mount
型号- FPC06302,H100XHXS,PDW08607,PDW08605,PDW08606,AEQ2234,B076MB6S,L288XC3S,PDW07630,AEQ03042,PDW08604,B148LA2S,B280LB0S,B280MD1S,L220XH5S,FPC07643,B056MB5S,B028LB7S,B099NC4S,B191KA1S,B080MB5S,B061MB6S,B033ND5S,PDW07069,B168MB1S,DEB-B274MB1S,DEB-B385MDOS,B083LB6S,L204XF4S,PDR05848,B119LB1S,B065NC5S,B210LA0S,AEQ03055,J30BLBA032LX1,B20BLSBN01,N016MD9S,FHC10290,FHC10291,FHC10292,FHC10293,B012MD5S,FHC10288,FHC10289,J30BJBA002LX3,AEQ05470,AEQ02199,AEQ05471,AEQ05472,B052NC5S,C079KB1S,AEQ05467,AEQ05468,AEQ05469,PDR06120,L157XG3S,B148QF0S,H140XHXS,B350NB2S,B105MB5S,PDW06984,PDR06390,B056RC4S,C142KB0S,PDW09692,B047MC5S,B094LA2S,FPC06630,B032ND5S,B102MC1S,FPC06078,B285LB2S,FPC06077,FPC06076,PDW07948,B115NB4S,B119MB1S,B111NC4S,B230LA0S,AEQ05246,L254XF3S,PDR06380,FPC06075,FPC06074,B042OD4S,FPC06073,B060NC5S,B142LA2S,B145LB1S,B380KA1S,B274MB1S,FPC06882,FPC06881,J30BJBA032LX1,B180MA1S,PDW06407,PDW06089,PDW06400,B192NB2S,PDW06401,H120XHXS,B220LA0S,B280LA0S,B280MC1S,N012ME9S,B118LB4S,B291MB0S,B070MB6S,FHC09097,B121MB4S,FHC09096,B040RG9S,B070NC5S,B393KD0S,J30BLBA002LX3,B095MB1S,B057MC5S,B20BHSBN01,FPC07183,FPC07182,B120MB1S,FPC07181,FPC07180,FPC06149,L128XH4S,FPC07234,AEQ3042,B024RF2S,B100MC5S,AEQ2199,FPC06701,FPC06700,DEB-B259MC1S,PDW08324,PDW08323,B031ND5S,B207LA0S,H080XHXS,B116NC5S,H168XHXS,FPC06154,FPC06153,PDW06933,AEQ3055,FPC07803,FPC07802,L065XG9W,L065XG9S,B138LA2S,B138MB1S,B190MB1S,FPC06152,B055NC5S,FPC06151,FPC06150,B200LA0S,PDW06011,J30BJBA022LX2,B058MD7S,AEQ2050,FPC06164,B28BJBFN01,PDW05758,B089NC4S,FHC09101,B028RF2S,FHC09102,AEQ05510,B260MB2S,FPC06719,B150OG0S,PDW06041,B385MD0S,B062MC55,L050XF9S,AEQ02234,AEQ06042,B149MC1S,B289KA0S,PDW06398,PDW06399,PDW06038,B381KD0S,J30BLBA012LX4,B040MB5S,B112MB1S,B240LA0S,FPC09291,B259MC1S,H160XHXS,B161LA0S,B081RC0S,B250LA0S,B280MF1S,L185XF4S,B096QC2S,FPC06913,B305LA0S,L157XF3W,L060XD9S,L095XG9S,B479KB0S,L185XF4W,B120RF0S,B039NC5S,FPC07337,B160KA1S,B279KB1S,J30BLBA022LX2,H182XHXS,B144MB1S,PDW07691,B038NC4S,B424MEZS,L117XH4S,B097MB0S,L117XH4W,B050ND4S,B016MD6S,B28BHBFN01,B28BTBFN01,B127MB2S,B165LA1S,J30BJBA012LX4,H060XHXS
Knowles Precision Devices Introduces the SFSW Series of Hermetic, Panel-Mount EMI Filters
Knowles Precision Devices has expanded EMI filter offerings to include hermetically sealed EMI filters that attenuate unwanted EMI signals while allowing desired signals to pass. SFSW series filters were designed to preserve signal integrity and ensure reliable operation in high-reliability applications with strict electromagnetic compatibility standards.
Knowles(楼氏电子)EMI滤波器选型指南
目录- General and Technical Introduction SM EMI Filters Panel Mount EMI Filters Discoidals, Planar Arrays and Special Filters
型号- SFAJL5000471MX,SFBDC5000220ZC,SFSUC5000150ZC0,SFBDT5000102MX,SFCMC5000333MX,SFBCC5000102MX,SFJGL5000224MX,SBSGC5000102MX,SFCDC5000681MX,SFBLL5000333MX,SFABL5000102MX,SFKKC5000330ZC,SFBML5000100ZC,SFAKT1000104MX,SFBML5000151MC,SFJNL2K00331MC,SFBCL5000681MX,SFCML5000221MC,SFJGL2K00471MC,SFKKT5000103MX,SFJNL2K00682MX,SFJGL1K00223MX,SFSUC5000680MC0,SFABC2000683MX,SFJGL1K00683MX,SFAKT5000681MX,SFBMC5000102MX0,SFABC5000103MX,SFBCL1000104MX,SFLMC1000104MX,SFBCP5000442ZX,SFBDT5000333MX,SFJNL2K00222MX,SFJGC2000105MX,SFJGP5000944MX,SFAJC5000472MX,SFBCP5000200ZC,SFAAC,SFCMC5000104MX,SFSUC5000683MX0,SFBDL5000470ZC,SFBCC5000333MX,SFKKC5000152MX,SFKKT5000101MC,SFCML5000683MX,SBSGC5000333MX,SFBDP5001N36MX,SFBDP5000443MX,SFBDC5000100ZC,SFBMP5000302MX,SFBDT5000331MC,SFTMC5000470ZC,SFABL5000333MX,SFBDT5000222MX,SFCDL5000471MX,SFBDC5000151MC,SFBDP5000201MC,SBSGC5000222MX,SBSMP5000152MX,SFAJC5000221MC,SFJNL2K00102MC,SFKKT5000332MX,SFKBL5000470ZC,SFKKL5000220ZC,SFLMP0500304MX0,SFAJC1000104MX,SFBCL5000101MC,SFBLL5000331MC,SFJGC5000334MX,SFCDL,SFCDC5000101MC,SFABL5000682MX,SFAJL5000153MX,SFBDP5000663MX,SFJGC3K00151MC,SFCDP,SFCMC5000222MX,SFJGC2K00472MX,SFKKT5000223MX,SFBML5000153MX,SFBCC5000150ZC,SFJNC2K00103MX,SFBCC5000682MX,SFBLL5000222MX,SFCDC,SBSMC5000472MX,SFABL5000150ZC,SFBDT2000473MX,SFBMT2000683MX,SFBMC5000472MX,SFCDC5000332MX,SFLMT5000100ZC,SFBCL5000332MX,SFLMC5000101MC,SFCDL1000474MX,SFJNL1000155MX,SFTMC5000333MX,SFLML5000680MC,SFAAC5000100ZC,SFCDC5000683MX,SFBCC2000473MX,SFKKL5000100ZC,SFABL5000680MC,SFLML5000153MX,SFKKT5000681MX,SFKKL5000151MC,SFABC5000101MC,SFAAC5000151MC,SFKKT5000221MC,SFBCC5000680MC,SFABL2000473MX,SFJNC0500335MX,SFTMC5000150ZC,SFSUC5000223MX0,SFCDP5000942MX,SFAKL2000683MX,SFCDL5000153MX,SFUMC5000220ZC,SFABC5000332MX,SFAKL5000332MX,1206Y1000103MXTE07,SFLML2000473MX,SFLMT5000151MC,SFLMC5000221MC,SFBLC5000332MX,SFBLC2000683MX,SFDPP0500944MX0,SFSRC5000220ZC0,SFAAC5000471MX,SFCMC5000102MX,SFLMP5000942MX,SFBDP5000301MC,SFCMC2000224MX,SFBCL2000683MX,SFCML5000681MX,SFAJC5000681MX,SFAJL5000100ZC,SFBLL5000102MX,SFCML5000472MX,SFKKT1000104MX,SBSPP1000682MX,SFBCL5000221MC,SFBDT5000150ZC,SBSGC5000682MX,SFAJL5000151MC,SFCDC5000221MC,SFBCP5000202ZX,SFLMC5000223MX,SFBML5000220ZC,SFABC5000223MX,SFJGP1K0136NMX,SFBDP5000203MX,SFKKT2000683MX,SFAKC5000470ZC,SFLMC5000332MX,SFCMC5000150ZC,SFKBL5000682MX,SFAAC5000153MX,SBSMC1000224MX,SFBDC5000153MX,SFJNC2K00332MX,SFLMT5000220ZC,SFAKT5000472MX,SFBLL5000150ZC,SFJGL5000104MX,SFLML5000471MX,SFSTC5000101MC0,SFJGC2K00103MX,SFAJL5000331MC,SFTMC,E01,SFBCP1000443ZX,E03,SFAKC5000152MX,SFAAC2000473MX,SFCDL5000102MX,E07,SBSGP5000222MX,SFBMC5000681MX,SFBMT5000220ZC,SFUMC0500154MX,SFJGL2K00331MC,SFUMC5000680MC,SFAJL5000682MX,SFKBL5000222MX,SBSGP0500224MXB,SFAJL5000222MX,SFBMP2000943MX0,SFKBC5000103MX,SFAJC2000683MX,SFJGP2K00302MX,SFKBL5000331MC,SFCDC5000154MX,SFKKC5000470ZC,SFBCC5000471MX,SBSMP5000472MX,SFJGL2K00682MX,SFBLC5000220ZC,SFABL5000471MX,SFKBC5000223MX,SFCMC5000473MX,SBSMC5000683MX,SBSMC5000223MX,SFJNC2000105MX,SFLML5000220ZC,SFJGL2K00222MX,SFAKL5000220ZC,SFTMC5000330ZC,SFBMP5000442MX,SFCML0500684MX,SFLMT2000683MX,SFBLC5000151MC,SFKBL5000102MX,SBSPP1000222MX,SFSUC1000334MX0,SFTMC2000473MX,SFCMC,SFAKT5000152MX,SFBML0500154MX,SBSGC5000473MX,SFCDL5000222MX,SFCML,SFBML5000471MX,SFAAC5000220ZC,SFAJC5000330ZC,SBSGP5000102MX,SFBLL5000680MC,SFJNL5000154MX,SBSMC5000332MX,SFUMC5000101MC0,SFLML5000151MC,SFCMC5000680MC,SFBMC1000104MX,SFJGL0500335MX1,SFBLC5000681MX,SFAKT2000683MX,SFLMC5000103MX,SFKBL2000473MX,SFBMT1000104MX,SFCDL5000331MC,SFBCC5000102MX0,SFBDT5000470ZC,SFAKL5000100ZC,SFJGP2K00942MX,SFLMC2000683MX,SFLML5000100ZC,SFLMT5000103MX,SFBLP0500943ZX,SFJGC2K00332MX,SFAKL5000151MC,SFAKL5000681MX,SFBLC5000100ZC,SFBMP5000662MX,SFCML5000103MX,SFKBL5000333MX,SFBMP5000940ZC,SFUMC5000151MC,SBSGC5000153MX,SFSTC5000472MX0,SFBMC5000330ZC,SFSTC5000102MX0,SFAJL0500154MX,SFKBL5000150ZC,SFKBC5000221MC,SBSPP1000102MX,SFBCL5000472MX,SFCMC5000331MC,SFBDT5000102MX0,SFUMC5000100ZC,SFCDL5000680MC,SFJGC0500335MX,SFAKL5000472MX,SFKBC5000101MC,SFBMT5000153MX,SFSUC5000332MX0,SFABL,SFBLC5000472MX,SFCDC5000472MX,SFBCP5000941ZX,SFBDL5000330ZC,SFBCL5000152MX,SFCDC5000152MX,SFABC,SFCDP5000302MX,SFAKL1000104MX1,SFJGC2K00681MC,SFBMT5000100ZC,SBSMC2000154MX,SBSMP2000104MX,SBSGP0500224MX,SFJNL1K00153MX,SFSRC0500473ZX0,SFAJL2000683MX1,SFBLC5000153MX,SFJGP2000205MX,SFBDP5000661MC,SFAKL5000153MX,SFJGL2K00102MC,SFKKL2000683MX,SFCDL5000682MX,SFBMP50013N6MX,SFBMT5000151MC,SFCML5000332MX,SFCDL5000473MX,SFKBC5000332MX,SFBDL5000152MX,SFBLP2000203ZX,SBSMC5000103MX,SFBMP5000202MX,SFAKT5000330ZC,SFBLL0500154MX,SFJNC3000684MX,SFJGL1000225MX,SFBDC2000683MX,SFUMC5000471MX,SFCML5000101MC,SFSUC5000220ZC0,SFBML5000680MC,SFAJL5000680MC,SFBLL5000682MX,SFBMC5000152MX,SFAKC5000330ZC,SFCML5000223MX,SFSTC2000473MX0,SFBDP5000441MC,SFJGC1K00333MX,SFAJC5000152MX,SFUMC5000153MX,SFCMC5000682MX,SFJGP1K00943MX,SFBDC5000331MC,SFBDT5000330ZC,SFLMT2000473MX,SFBDC5000222MX,SFBDP5000941MX,SFCDP5000661MC,SFBCC5000151MC,SFCDP5000201MC,SFBCC5000100ZC,S
PCB Design Considerations for High-Performance Filtering in mmWave Applications
RF circuits for applications in the mmWave range (30 to 300 GHz) require high-performance filtering to meet the high-data, high-speed functionality that operating at these higher frequencies promises. However, filters for devices operating in the mmWave range will not function optimally if your printed circuit board (PCB) is not configured appropriately. To address these complex issues, when starting a new circuit design for a mmWave application, Knowles recommends carefully evaluating the following design factors for your PCB assembly
The Role of EMI Filters in Power Electronics
EMI filters are designed to keep internally generated electrical noise from conducting across the system and negatively impacting operations elsewhere. In other words, they contain and manage noise. In power electronics, they take the form of power line filters that protect the line from upstream noise.
How to Use the Different Frequency Dependencies to Manipulate Impedance and Create Various Filter Responses?
Knowles covered how RF designers can use the different frequency dependencies of capacitors and inductors to manipulate impedance and create various filter responses.
Knowles‘ Microstrip Filters Offer a High Repeatability and Temperature Stability from -55℃ to 125℃
Since Knowles acquired Integrated Microwave Corporation (IMC) in 2020, Knowles has an extended its range of RF and microwave filtering solutions to include a wide variety of ceramic coaxial resonators, lumped element filters, and cavity filters from the VHF to the Ka-band.
滤波器类型SFSWR焊接安装密封EMI滤波器(3.25mm主体直径,玻璃密封底端)数据表
描述- 本资料为SFSWR系列Solder Mount Hermetic EMI Filter的详细数据手册,介绍了该系列滤波器的电气和机械特性,包括电容值、额定电压、电流额定值、绝缘电阻、温度范围、封装尺寸、重量等,并提供了不同型号的产品代码和参数。
型号- SFSWR5000331MC0,SFSWR5000102MX0,SFSWR5000221MC0,SFSWR5000100ZC0,SFSWR5000472MX0,SFSWR5000682MX0,SFSWR5000471MC0,SFSWR,SFSWR5000103MX0,SFSWR5000680ZC0,TYPE SFSWR,SFSWR5000681MX0,SFSWR5000330ZC0,SFSWR5000222MX0,SFSWR5000151MC0,SFSWR5000101MC0,SFSWR2000223MX0,SFSWR1000333MX0,SFSWR5000220ZC0,SFSWR5000332MX0,SFSWR2000153MX0,SFSWR1000223MX0,SFSWR5000470ZC0,SFSWR5000152MX0
SFAK馈通EMI滤波器数据表
描述- 本资料为Syfer Technology Ltd.生产的SFAK系列通孔EMI滤波器数据手册。该手册详细介绍了不同型号的滤波器的电气和机械规格,包括电容值、电感、额定电压、绝缘电阻、温度范围等。同时提供了安装指南,包括焊接过程、固定扭矩、接地要求等内容。
型号- SFAKC5000150ZC,SFAKT5000101MC,SFAKL5000152MX,SFAKT5000680MC,SFAKL5000221MC,SFAKC5000152MX,SFAKL5000150ZC,SFAK.SFAKT5000102MX0,SFAKT1000104MX,SFAKT5000331MC,SFAKT5000153MX,SFAKC5000223MX,SFAKL5000472MX,SFAKT5000151MC,SFAKT5000333MX,SFAKC5000681MX,SFAKC5000471MX,SFAKL5000222MX,SFAKC5000100ZC,SFAKC5000331MC,SFAKL2000473MX,SFAKC5000102MX,SFAKL5000330ZC,SFAKL2000683MX,SFAKC5000333MX,SFAKL5000103MX,SFAKL0500154MX,SFAKL5000332MX,SFAKT5000681MX,SFAKT5000223MX,SFAKT5000100ZC,SFAKC5000221MC,SFAKT5000471MX,SFAKC0500154M,SFAKL5000220ZC,SFAKT5000102MX,SFAKL5000470ZC,SFAKL5000682MX,SFAKL1000104MX,SFAKC1000104MX,SFAKT5000221MC,SFAKC5000153MX,SFAKC5000151MC,SFAKT5000150ZC,SFAKT5000152MX,SFAKL5000680MC,SFAKL5000153MX,SFAKL5000101MC,SFAKL5000331MC,SFAKC5000682MX,SFAKL5000223MX,SFAKC5000222MX,SFAKC5000472MX,SFAKT5000332MX,SFAKC5000220ZC,SFAKC2000473MX,SFAKC5000470ZC,SFAKT5000330ZC,SFAKT2000683MX,SFAKC5000103MX,SFAKC5000332MX,SFAKL5000102MX,SFAKT5000682MX,SFAKT5000222MX,SFAKC5000330ZC,SFAKC2000683MX,SFAKL5000100ZC,SFAKL5000333MX,SFAKT5000472MX,SFAKC5000101MC,SFAKT2000473MX,SFAKT5000220ZC,SFAKC5000680MC,SFAKT5000470ZC,SFAKL5000471MX,SFAKT5000103MX,SFAKT0500154MX,SFAKL5000151MC,SFAKL5000681MX
Knowles Microstrip Filter Helps Your Thin Film RF Devices to Achieve the Best Performance
It’s clear that filters designed using thin film have several key advantages, especially for RF devices operating at high frequencies. But to fully utilize these advantages, you need to be careful about the material properties of your selected substrate.
滤波器类型SFSWG焊接安装密封EMI滤波器(3.25mm主体直径,玻璃密封法兰端)数据表
描述- 本资料为SFSWG系列Solder Mount Hermetic EMI Filter(Solder焊接式密封EMI滤波器)的产品数据表。产品采用C滤波电路配置,具有高绝缘电阻、宽温度范围和良好的密封性能。资料详细列出了不同电容值、电压等级和封装尺寸的产品规格,并提供了订购信息。
型号- SFSWG5000471MC0,SFSWG,SFSWG1000223MX0,SFSWG5000151MC0,SFSWG1000333MX0,SFSWG5000220ZC0,SFSWG5000101MC0,SFSWG2000153MX0,SFSWG5000330ZC0,SFSWG5000680ZC0,SFSWG5000102MX0,SFSWG5000103MX0,SFSWG2000223MX0,SFSWG5000681MX0,SFSWG5000682MX0,TYPE SFSWG,SFSWG5000470ZC0,SFSWG5000221MC0,SFSWG5000332MX0,SFSWG5000222MX0,SFSWG5000100ZC0,SFSWG5000472MX0,SFSWG5000331MC0,SFSWG5000152MX0
Switch Filter Banks for Agile RF Receiver Design in Radar
This is the third installment in our RF Components for Radar series. In the first installment, we provided an overview of the key functional units in radar, including duplexing, filtering, power amplification, waveform generation, low-noise amplification (LNA), receiving and analog-to-digital conversion (ADC). Here, we’ll focus on a particular form of filtering technology: switch filter banks.
B100RH2W 2-18GHz带通滤波器
描述- 该资料介绍了Knowles公司生产的B100RH2W型号的2-18GHz带通滤波器。这款滤波器采用多层滤波技术,具有小型化设计,适用于宽频段应用。资料提供了详细的电气规格、尺寸、封装信息和订购指南。
型号- B100RH2W-T,B100RH2W
B084MC6S 8.42GHz表面贴装带通滤波器
描述- 该资料介绍了Knowles Precision Devices公司生产的8.42GHz表面贴装带通滤波器B084MC6S。该滤波器采用低损耗、温度稳定的材料,具有小型化设计,性能随温度变化小,适用于多种频率带,提供高度可重复的性能。
型号- B084MC6S,B084MC6S-T
电子商城
现货市场






































































































































































































登录 | 立即注册
提交评论