Evaluating BLE vs Wi-Fi: Which is the Best Connectivity for IoT Development?




The tech space is rapidly evolving, and IoT is at the heart of it. Two big players in this scene are BLE, a power-saving version of Bluetooth designed for short connections, and WiFi, which many of us use daily for internet access. By selecting the best IoT connectivity, businesses that wish to create their own IoT hardware stand to gain substantially from delivering IoT products that are innovative and ahead of the competition.
Both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi have their own advantages. Wi-Fi is best for projects involving several devices dispersed over greater distances and demanding high data rates, whereas Bluetooth excels in terms of battery consumption, security, and some dedicated usage. But before you make a decision on the best IoT protocols for a given IoT solution, let us study the two communication technologies in detail:
How Are BLE and Wi-Fi Different?
WiFi is a local wireless network that runs on the 802.11 standards set forth by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). Bluetooth Low Energy (Bluetooth LE, colloquially BLE, formerly marketed as Bluetooth Smart) is a wireless personal area network technology designed and marketed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (Bluetooth SIG).
Basic Introduction to Wi-Fi
WiFi enables two devices to interact with one another by using radio waves (RF). It is most commonly used to connect Internet routers to devices or connect two hardware components together. Both the 2.4GHz UHF and 5GHz SHF ISM radio bands are available for use with WiFi.
Basic Introduction to BLE
BLE is often used in small devices like fitness trackers, smartwatches, and other connected devices to wirelessly communicate data without severely impacting the battery life. For data transfer, Bluetooth uses UHF radio waves.
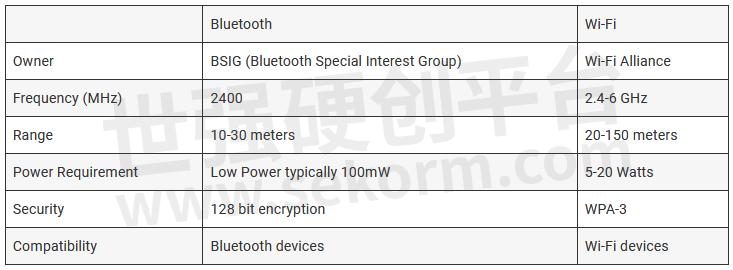
Security & Privacy
When compared to Wi-Fi, BLE is always thought to have better security and data privacy. Both the transmitter and the receiver are aware of the data exposure in a peer-to-peer connection. Wi-Fi, in contrast, does not request user consent before exchanging data.
I’d like to use an analogy: for Wi-Fi, stores can get your phone’s data even if you didn’t say it’s okay. The only way to stop this is by turning off the WiFi on your phone. This is like saying “No” after someone’s already started doing something. For BLE, you have first to download an app and say it’s okay for the app to find BLE beacons. This is like saying “Yes” before anything happens. Online marketing has shown that people like to choose what data they share. But, if stores don’t care about this, WiFi can get data from more people because they don’t need an app.
To enhance the security, both take action to fix security holes. Bluetooth uses AES 128-bit encryption to ensure data security. With proper setup and the passkey ‘pairing method,’ BLE connections become secure.
Wi-Fi uses 256-bit encryption and has well-established security protocols including WEP, WPA, WPA2, and WPA3. WPA3 is the most advanced of them, which is perfect for the transfer of sensitive and important data.
Precision
BLE stands out for its precision in the indoor positioning field. While Wi-Fi wasn’t designed primarily to gauge the distance between devices, it can make attempts. both of them employ RSSI to pinpoint locations. BLE offers greater accuracy and consumes less power, making it possible to create a variety of BLE beacon hardware options. Here is a quick comparison of how well they performed in indoor positioning.
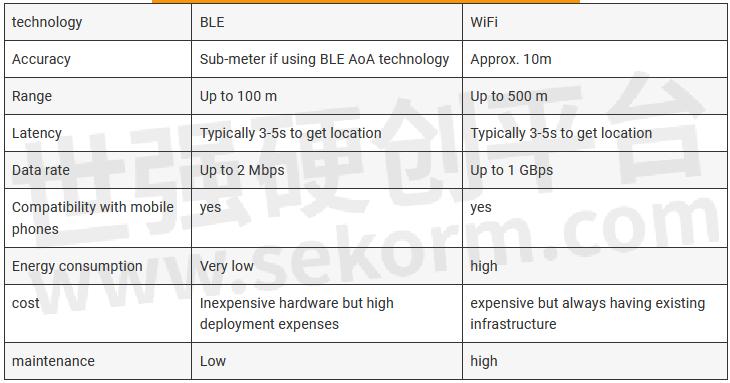
BLE is known to achieve a higher degree of location accuracy and requires significantly less power. Yet, many entities already possess Wi-Fi setups that can be repurposed for indoor positioning. Modern buildings, particularly workplaces, may include dozens or even of hundreds of access points to ensure robust WiFi access. In contrast, deploying BLE might necessitate the incorporation of fresh beacons and sensors.
So which one should be adopted? The choice ought to be based on your actual demands. Bluetooth is undoubtedly the most accurate option if you want to engage customers based on their position or offer an inside navigation experience.
Deployment Costs
Although linking low-power BLE sensors to the cloud seems like a great concept, we also need to take the ROI into account. Is the hassle worthwhile? To connect non-IP devices like sensors to the cloud, BLE requires gateways to be deployed strategically all around an area. In contrast, WiFi enables direct IoT sensor connections to IP networks. Since many commercial buildings already have WiFi installed, integrating IoT is possible without incurring additional expenses for new equipment. Due to this, WiFi may be more economical for larger deployments.
However, a Bluetooth gateway is still the best choice in some specialized and specialized IoT applications (such as creating a secure and closed network or remote sensor installation). The combination of an existing WiFi network and a dedicated BLE network remains an option for decision-makers, and it frequently proves to be the more scalable and financially sensible option for large-scale IoT projects.
Speed
BLE focus is on low energy consumption, which is reflected in its data rate. The typical BLE connection speed ranges from 1 Mbps to 2 Mbps, which is suitable for many IoT devices that only handle small amounts of data. Receiving brief data updates every few seconds is a task for which BLE is especially well suited. Examples include information about acceleration, temperature data from sensors, and heart rate monitors.
However, Wi-Fi could be used if you need to send data to a server immediately or have other bandwidth-intensive data needs. It’s utilized by many IoT devices. WiFi technology is capable of transmitting data at a speed of up to 1.3Gbps. This makes it the best choice for transferring larger files and data. But Wi-Fi networks use the TCP-IP protocol, which necessitates that every device get an IP address and authenticate itself on the network. Not all IoT devices will work with this. Wi-Fi networks, on the other hand, have extremely fast data throughput, but IoT devices don’t always require it.
Advantages of BLE over WiFi
As you can see there are numerous characteristics you should consider
when choosing between BLE or Wi-Fi. If you wish to connect low-power
IoT devices like simple sensors, BLE is a significantly more practical
alternative because it is intended to deliver short data packets. There
are distinct advantages when using BLE over WiFi:
Extended Battery Life
BLE has been specifically designed for minimal power consumption, making it a top choice for devices that rely on battery power. Be it a fitness tracker, a smartwatch, or a health monitor, BLE ensures that these devices don’t drain their batteries quickly. In contrast, WiFi, with its broader range and higher data transfer capabilities, tends to use more energy. This means devices using BLE can go longer between charges, providing users with more uninterrupted usage.
Instant Connection
Time is of the essence in the digital world. BLE stands out in its ability to establish connections almost instantly. This rapid connection time is vital for applications that require frequent, short bursts of data transfer, such as updating a heart rate on a fitness tracker or sending a command to a smart home device. While WiFi is incredibly robust and excellent for sustained connections, it can sometimes take longer to establish a connection, especially when first connecting to a network.
Cost-effectiveness in Certain Applications
Not all wireless applications require the high data rates and extended range WiFi provides. BLE can be a more cost-effective solution in scenarios where short-range, low-data rate communication suffices. The hardware for BLE is often cheaper, and its simpler setup means fewer costs related to infrastructure and maintenance. BLE presents a cost advantage for businesses and developers working on specific applications like beacons for an indoor location or simple sensor data collection without compromising performance.
Advantages of Wi-Fi over BLE
WiFi uses a high-bandwidth connectivity technology with a long range. It facilitates the creation of a direct internet connection and works with more fixed devices. Additionally, for the majority of projects, an intermediary device like a BLE to WiFi bridge will be needed because a Bluetooth device alone cannot transmit the data received. Continue reading to learn more about WiFi’s advantages versus BLE:
Higher data transfer rates
One of WiFi’s most notable strengths is its ability to quickly transfer large chunks of data. WiFi boasts significantly higher data transfer rates than BLE, whether updating firmware on a smart thermostat or sending high-resolution surveillance camera footage. This ensures seamless device communication, efficient updates, and an overall improved user experience.
Wider coverage areas
WiFi isn’t just about speed; it’s also about reach. The range of WiFi networks is generally much wider, encompassing entire houses, offices, or even large outdoor areas in some cases. This extended coverage makes it ideal for environments where users move around a lot, ensuring they remain connected.
Established Infrastructure and Widespread Adoption
Take a moment to consider the places you’ve accessed WiFi – homes, coffee shops, airports, hotels, and even some public transportation. Its established infrastructure and widespread adoption mean users can reliably find and connect to WiFi networks worldwide in many urban areas. This universality is not just convenient; it’s pivotal for activities that require steady, high-speed internet connections.
BLE and WiFi in IoT Development
As technology hurdles forward, BLE and WiFi stand at the forefront of wireless innovation. The coming years promise even lower energy consumption for BLE, making it a cornerstone for energy-efficient IoT devices. At the same time, its potential in location-based services could redefine sectors like retail and healthcare. Conversely, the evolution of WiFi is geared towards achieving lightning-fast speeds and broader ranges, addressing the modern consumer’s hunger for consistent, ultra-fast internet connectivity, especially in our remote-centric world.
IoT projects have different needs for things like power utilization, bandwidth use, and range. The key differentiator you need to tilt the odds of the success of your IoT project in your favor may be the connectivity of your devices through appropriate interoperable, effective connectivity solutions.
To connect with a Bluetooth-enabled device, an IoT device requires the following:
A microprocessor for Bluetooth to function, such as BLE SoCs;
A second device is necessary for pairing;
A battery or low-energy power source;
For the gadget to transmit a signal, it must be in close proximity.
A Wi-Fi IoT device needs to meet the following compatibility requirements for widespread adoption in IoT applications:
A WiFi SoC is required for WiFi to function;
A firmware to manage WiFi credentials and security;
A WiFi access point must be nearby for the devices to work;
Fixed and stationary IoT hubs are preferred to establish connectivity.
Converge BLE and Wi-Fi
Consumer demands are shaping this trajectory as much as the technological advancements themselves. A world that’s more connected than ever is driving the need for devices that are both powerful and efficient. People want BLE that integrates seamlessly into their daily lives and robust WiFi, no matter the number of devices or environmental challenges. Dusun IoT has a wide range of Bluetooth WiFi Gateways to use in conjunction, allowing users to use both future-proof technologies to build a strong future.
Final Words
The future landscape of BLE and WiFi seems boundless. Adapting rapidly to our changing world, these technologies signal a future of intuitive, high-speed, and seamless connectivity. The promise is clear: a wireless world tailored to every individual need.
- |
- +1 赞 0
- 收藏
- 评论 0
本文由出山转载自Dusun Blogs,原文标题为:Evaluating BLE vs Wi-Fi: Which is the Best Connectivity for IoT Development?,本站所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源,不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
相关推荐
蓝牙片上系统如何应用到物联网智能家居/可穿戴设备?
BLE SoC是一种将多个组件集成到单个芯片上的BLE芯片。这允许更紧凑和有效的设计,因为所有必要的组件都包含在单个芯片上。BLE SoC广泛应用于物联网网关,参与各种物联网项目。
Wi-Fi BLE IoT Module: Bridging the Gap in IoT Connectivity
This article delves into the intricacies of the Wi-Fi BLE IoT Module, exploring its functionality and how it revolutionizes IoT connectivity. Furthermore, this article will also delve into the various applications of the Wi-Fi BLE IoT Module across industries, showcasing its versatility and adaptability in a wide range of scenarios.
Key Applications of IoT Modem in Industrial Automation
This article will explore in detail the key applications and functional advantages of IoT Modem in industrial automation, and analyze its application effect in practical scenarios through specific case studies.
通量科技(FLUXWORKS)射频前端芯片选型指南
目录- 低噪声放大器 增益放大器 驱动放大器 射频功率放大器 射频开关 可变增益放大器 射频无源器件 射频接收前端模组 IoT射频模组
型号- FW2104,FW2106,FW2305,FW2101,FW3112,FW2102,FW3115,FW2103,FW2301,FW3114,FW2306,FW51,FW51系列,FW94,FW11系列,FW11,FW1103,FW2435,FW5105,FW5106,FW5103,FW1102,FW5104,FW21系列,FW81,FW1108,FW1109,FW43,FW45,FW9343,FW4503,FW1115,FW2204,FW4502,FW1116,FW2205,FW1117,FW2206,FW1112,FW2201,FW4501,FW1113,FW2202,FW2409,FW2207,FW2208,FW2209,FW2407,FW31,FW31系列,FW94系列,FW2202E,FW81系列,FW2210,FW4312,FW3101,FW4311,FW3104,FW3103,FW4313,FW4511,FW22系列,FW43系列,FW24系列,FW45系列,FW22,FW21,FW24,FW9443
Bluetooth®信道探测
描述- 本文介绍了Silicon Labs的蓝牙通道声测技术,该技术提供高精度距离测量,支持相位和往返时间测量方法。文章详细阐述了蓝牙通道声测的原理、应用场景、性能特点和安全特性,并展示了相关开发工具和软件支持。此外,还比较了蓝牙通道声测与其他蓝牙LE定位技术的差异,突出了其在室内定位、资产管理和静态设备定位等领域的优势。
型号- EFR32MG24,EFR32XG24,XG24,XG24-DK2606A,BG24,BRD4198A,XG24-PK6036A,EFR32MG24B210F1536IM48-B,BRD2606A,XG24-RB4198A
安信可科技(Ai-Thinker)物联网专用模组&天线选型指南
目录- LoRa product Radar product WiFi+Bluetooth products 2.4G Series Module GPS Series Module UWB & 4G series module GPRS series module Offline Voice Module Series Antenna
型号- RA-01SH,PB-02-KIT,RTL8720 SERIES,AI-WB1,AI-WB2,AI-WB2-M1,HI-07S-KIT,TB-02-KIT,AI-WB2-12F-KIT,AI-WB2-13-KIT,AI-WB2-13U,AI-WB2-01S,A9,SX1268,RA-01SC,TG-02-KIT,PB SERIES,RTL8710BX SERIES,GPS SERIES,AI-WB2-01M,VC-01-KIT,HI-12F,TB SERIES,HI-12F-KIT,BW16,AI-WB2 SERIES,BW15,BW14,TG-12F-KIT,BW12,RTL8710BX,A9G,HI SERIES,AI-WB2-12S,PB-03,SX126X,AI-WB1-32S,HI-07S,HI-07SL-KIT,PB-01,PB-02,RG-02,AI-WB1-32S-KIT,RTL8720DN,AI-WB2-12F,TG-01M,AI-WB1SERIES,NF-05,NF-02-PA,NF-04,NF-03,BW16-KIT,NF-01-S,SX127X,TB-03F-KIT,LLCC68,TG-02,AI-WB2-07S,NF-01-N,NF-02-PE,AI-WB1-32S-CAM,GP-02-KIT,AI-WB2-M1-I,TG-02M-KIT,TG-02M,RA-08-KIT,GP-01,GP-02,CA-01-KITC,CA-01,2.4G SERIES,AI-WB2-13,PB-03F,PB-03M,TG SERIES,TB-04-KIT,TB-05,GPRS SERIES,TB-04,TG-02F,TB-02,RTL8720DN SERIES,TG-02F-KIT,4G SERIES,PB-03M-KIT,AI-WB2-32S-KIT,BU01,RA-01,PB-03-KIT,ESP32-G,RTL8720,RA-08H,NF-04-MI,VC-02-KIT,NF-05-S,RA-01S,HI-12FL,RA-01H,HI-07SL,AI-WB2-32S,RA-01SCH,PB-01-KIT,RTL8720CF,TG-01M-KIT,TG-12F,AI-WB1-A1S,AI-WB1-12F,TB-03F,BW15-KIT,GPRS,UWB SERIES,GP-01-KIT,AI-WB1-12F-KIT,NODEMCU-BU01,RA-08H-KIT,RD-01,RA-02,RTL8720CF SERIES,RA-08,VC-02,VC-01,HI-12FL-KIT,PB-03F-KIT
【经验】多协议无线 SOC EFR32MG实现ZigBee的OTA操作指南
EFR32MG系列是Silicon Labs公司推出支持多协议无线 SOC,可以单芯片支持私有协议、BLE5.0、BLE MESH、ZigBee和Thread协议,并且可以单芯片支持Sub-GHz和2.4GHz的频段。由于其超低功耗、高射频性能以及高集成度等特点被广泛应用于智能家居、安防、智能工业等市场。在ZigBee的实际应用中,OTA是必不可少的功能,由于选择的型号不同,配置OT
BW20-12F 规格书
描述- 深圳市安信可科技有限公司推出的BW20-12F是一款基于RTL8711系列芯片开发的双频Wi-Fi + BLE SoC模块,支持2.4GHz和5GHz双频段,具备丰富的外设接口,适用于物联网、移动设备、可穿戴电子设备、智能家居等领域。
型号- BW20-12F
Silicon Labs(芯科科技) 物联网无线产品选型指南
目录- Company and product overview Bluetooth Modules Bluetooth Modules Overview Bluetooth Modules Bluetooth Low Energy Kits Bluetooth Modules Blue Gecko Wireless Modules Bluetooth Modules Bluetooth Xpress Modules Bluetooth Modules Blue Gecko Wireless SoCs Bluetooth Modules Bluetooth BR/EDR Kits Bluetooth Modules Bluetooth BR/EDR Modules proprietary wireless devices proprietary wireless devices Proprietary Kits Proprietary Wireless Sub-GHz and 2.4 GHz Dual Band Devices Proprietary Wireless Sub-GHz Devices Wi-Fi Modules Wi-Fi Modules Wi-Fi Kits Mighty Gecko Modules Mighty Gecko Modules Mighty Gecko Development Kit Mighty Gecko Modules Mighty Gecko Mesh Networking Wireless SoCs Z-Wave Modules Z-Wave Modules Z-Wave Reference Designs Z-Wave Modules Z-Wave Development Kits
型号- EBWT41U,ZDB5202,SLEXP8027A,EFR32FG13P233F512GM48,EFR32™,SLWSTK6061B,MGM12P,EZR32WG,EFR32FG13P231F512GM32,EFR32BG12P232F1024GM68,EFR32MG13P733F512GM48,EFR32BG13P532F512GM32,WT12,AMW007-E04,EFR32,WT32I,EZR32™,BGM121,BGM11S,WT11U,EFR32FG,EFR32FG14P233F256GM48,SLWSTK6062B,RBK-ZW500DEV-CON2,SLWSTK6120A,SLWSTK6063B,RBK-ZW500,EFR32BG12P132F1024GL125,SI4XXX,ZM5101,ZM5304,ZDB5101,ACC-UZB3-U-BRG,BGM111,EBWT11U,EFR32FG14P233F128GM48,ACC-UZB3-U-STA,MGM111,ZDB5304,SLWSTK6000B,SLWSTK6020B,WT32,SI10XX,SLWSTK6101C,EFR32MG13P632F512GM32,AMW037,EFR32FG12P433F1024GM48,DKWT32I-A,EFR32MG12P132F1024GL125,EFR32MG1P133F256GM48,BGM13S,EZR32HG,BGM13P,BGX13P,EZR32LG,MGM13P,WT41U,EFR32BG13P733F512GM48,BGX13S,SLWSTK6060B,MGM13S,SLWSTK6065B,WGM110,RBK-ZW500DEV-EMB2,EFR32BG12P433F1024GL125,EBWT12-A,ZM5202,AMW007,SLTB004A,EFR32MG14P733F256GM48
【选型】骏晔科技(DreamLNK)无线模块(ASK模块/FSK模块/2.4G模块)选型指南
目录- ASK模块 FSK模块 2.4G模块 无线模块行业应用
型号- DL-RXC2015 315M,DL-RTS4438B 433M,SI4438,DL-RTS4432 433M,NRF24L01P,SI4432,DL-24N,DL-TXR25 433M,DL-24TR,DL-RTC1101 PA433M,DL-RX06C-LO6433M,DL-RXC6B 433M,DL-BK24K6-RX,DL-RX06C-KO4,DL-TXR25 390M,DL-RTS4432 433M,DL-RXC2016BH 315M,CC1101,DL-BK24K6-TX,DL-RX06C-LO6,DL-RXC6B,DL-RXC2015 433M,DL-TX19-S 433M,DL-TX19,DL-TXR25 315M,RFX2401C,SI4463,NRF24L01,DL-TXR25,DL-RTS4463 433M,DL-24PA,DL-24NPA,DL-RXC2016BH 433M,DL-RTC1101 433M,DL-RXC6B 315M,M-AF119MPA 433M,DL-BK24K6-52TX,DL-TX19-S 315M,CC2500
芯科SiWx917低功耗WiFi 6+BLE SoC用于IPC网络摄像机,支持低功耗WiFi保活功能
一些电池供电的IPC在实际应用中,往往面临功耗高、网络连接慢以及处理能力有限等挑战。SiWx917 SoC,Silicon Labs超低功耗Wi-Fi 6和蓝牙 BLE 5.4无线SoC芯片,非常适合应用。
【视频】2023年3月16日射频微波器件与材料新技术研讨会
Ignion、史密斯英特康、德聚等分享电磁屏蔽CIPG、毫米波传感器SoC、雷达传感器芯片等新品及方案。
ESP-S3-32S规格书
描述- 本资料为ESP-S3-32S模块的技术规格说明书,详细介绍了该模块的概述、配置、主要参数、外观尺寸、管脚定义、原理图、天线参数、设计指导等内容。ESP-S3-32S是一款集成了WiFi和蓝牙功能的低功耗系统级芯片(SoC),适用于物联网(IoT)、移动设备、可穿戴电子设备和智能家居等领域。
型号- ESP-S3-12K,NODEMCU-ESP-S3-12K,ESP-S3-32S,ESP32-S3,NODEMCU-ESP-S3-32S
蓝牙网关市场热门产品选购宝典,帮助您筛选出最适合的物联网网关
在本文中,我们将探讨不同类型的蓝牙网关及其分类,并提供一份指南,帮助您筛选出最适合的物联网网关。
电子商城
服务
支持 3Hz ~ 26.5GHz射频信号中心频率测试;9kHz ~ 3GHz频率范围内Wi-SUN、lora、zigbee、ble和Sub-G 灵敏度测量与测试,天线阻抗测量与匹配电路调试服务。支持到场/视频直播测试,资深专家全程指导。
实验室地址: 深圳/苏州 提交需求>
Ignion可支持多协议、宽频段的物联网天线方案设计,协议:Wi-Fi、Bluetooth、UWB、Lora、Zigbee、2G、3G、4G、5G、CBRS、GNSS、GSM、LTE-M、NB-IoT等,频段范围:400MHz~10600MHz。
最小起订量: 2500 提交需求>
































































































































































































登录 | 立即注册
提交评论