Signal Generators: The Different Types and How They Work




In electronics, signals are analogous to speech. Just as we exchange information through conversation, electronics at all levels talk via signals — from microscopic transistors on tiny integrated circuits up to consumer devices and large systems like satellites.
Being this ubiquitous means that in every industry, a substantial part of electronics testing goes into getting the signals right, and signal generators are the workhorses that make it possible.
In this article, explore:
· the different signals out there
· the types of signal generators and what they do
· prominent applications of signal generators
· the key features and specifications you must consider when selecting one
· the internals of signal generators
What are signals?
To understand signal generators, we must first understand signals and their associated terminology.
Signals are a technique of conveying information or commands by encoding them as changes in electrical properties like voltage, current, frequency, phase, or power.
Voltage changes are the most common signaling technique. However, changes in other properties are also used, as seen in these examples:
· Current signaling: The 4-20 mA current loop, a common signaling technique in industrial process control, works by varying the current.
· Power signaling: In fiber optics, intensitymodulation is a technique of encoding information as changes in the power of the light signal.
· Phase signaling: Wi-Fi networking uses techniques like phase shift keying to convey data through changes in the wave's phase.
Apart from the electrical properties they rely on, signals are also characterized by their waveforms.
What are signal waveforms?
The changes in electrical characteristics over time for signaling purposes follow common shapes called waveforms.
One common waveform is the sine wave, widely used in radio frequency (RF) and power supply applications.

Fig 1. Sine waveform
Another common waveform is the square wave, a core element of clock signals as well as digital signals that encode information in binary as combinations of zeros and ones.

Fig 2. Square waveform
When the flat peak of the square wave is at a certain voltage level (like 5 or 3.3 volts), it's interpreted as on, or one, and anything below a threshold is seen as an off, or zero.
The triangle waveform is also common. For example, it's widely used for pulse width modulation in power, battery charging, screen brightness, and lighting circuits of consumer electronics and automobiles.

Fig 3. Triangle waveform
A fourth common shape is the sawtooth, a right-angled triangle that resembles the tooth of a saw. An example of its use is automotive radar chirp sweeps over a frequency range.
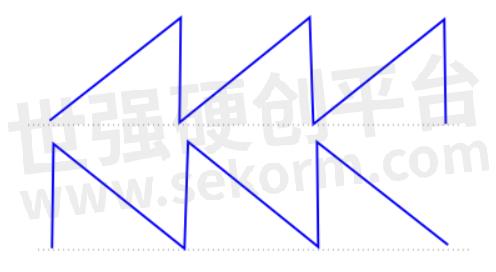
Fig 4. Sawtooth waveform
However, waveforms aren't limited to these common ones. These are just the simple building blocks. By combining them and adding modulation schemes, far more complex waveforms, like the ones below, are generated to scale up the complexity and capacity of the information being sent over them.
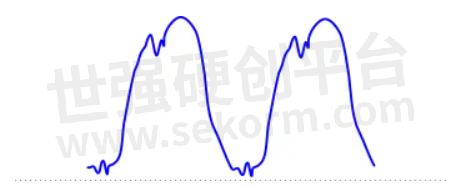
Fig 5. Arbitrary waveform
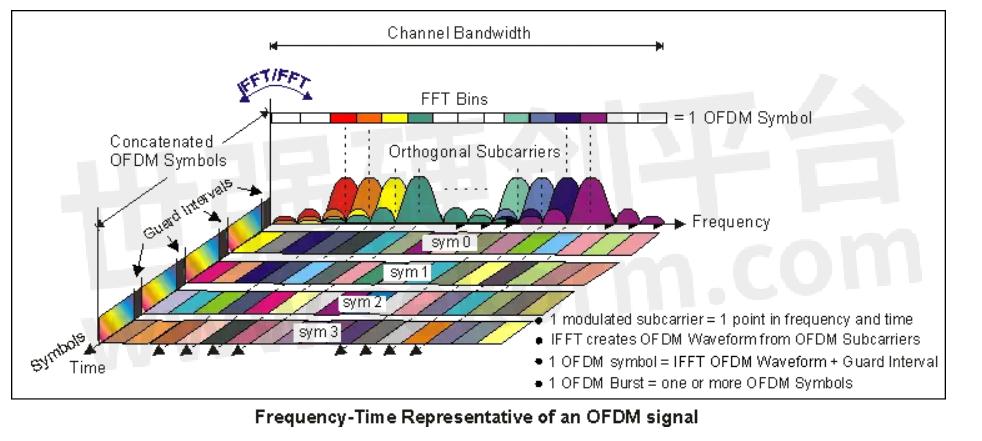
Fig 6. Sinusoidal signals are combined using orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing for mobile and Wi-Fi communications
With this essential knowledge of signals, we can start learning about signal generators.
What are signal generators?

Signal generators are devices that simulate various signal waveforms and modulation formats to test equipment and circuits for signaling problems. They're used extensively for checking a wide range of equipment, including mobile base stations, radars, oscilloscopes, and more.
Signal generators enable engineers to:
· shape complex signals by combining multiple waveforms
· vary electrical properties like frequency and phase
· add modulation schemes
· encode information and verify data integrity during transmission
What are the types of signal generators?
A variety of signal generators exist with different generating capabilities. We look at the major types below.
1. Signal generators
The term, signal generator, can mean different things depending on the context. One meaning is an umbrella term for any device that can generate signals.
But the other usage is more restricted to imply a generator that only creates sinusoidal signals but with other specialized capabilities, as explained next.
2. RF signal generators and microwave signal generators
Both RF and microwave signal generators are specialist devices for RF applications like:
· mobile communications
· Wi-Fi networking
· radars
· military and defense communications
The primary difference between these two types of RF generators is in their operating frequency range.
RF signal generators typically start from a few kilohertz (kHz), cover the common RF frequencies like 3-120 megahertz (MHz) for radio broadcasting, and go up to 6-9 gigahertz (GHz) covering Wi-Fi communications and older mobile communication standards like 3G and 4G.
In contrast, microwave signal generators are high-frequency generators. Their upper limit can go up to 300 GHz, but 30-110 GHz are more common. They enable the testing of 5G and 6G mobile communications, military radar systems, and automotive radars.
Both types of RF generators can be further classified as either vector or analog signal generators.
Vector signal generators produce modulated signals with precise control over both amplitude and phase using state-of-the-art digital generation techniques.
This makes them particularly useful for testing modern RF receivers that involve complex modulation formats like quadrature amplitude modulation with orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM).
The vector in their name comes from the representation of amplitude and phase as vectors in the in-phase and quadrature plane (I-Q plane).
Analog signal generators
Analog signal generators are simpler generators that produce RF signals using basic analog techniques with straightforward frequency or amplitude modulation.
Function generators are simple general-purpose signal sources that can produce repeating and non-repeating basic waveforms like sines, squares, and triangles.
They're useful for testing printed circuit boards, audio devices, and low-end test equipment like low-frequency oscilloscopes.
4. Arbitrary function generators
Arbitrary function generators are more versatile than plain function generators. They provide more control over the waveforms by enabling users to vary frequencies, amplitudes, and offsets. They can also add simple modulation schemes and basic noise profiles.
5. Arbitrary waveform generators
Arbitrary waveform generators are the most capable type of general-purpose function generators. They provide an enormous degree of control over waveforms with features like:
· combining multiple complex waveforms
· replaying recorded waveforms
· customized sequencing of waveforms by manipulating them with triggers, jumps, and loops
These specialist signal generators produce digital square wave signals with high and low states for testing digital signals and protocols. They provide control over voltage levels, duty cycles, and encoded information. They're used for testing digital circuits and digital signals like:
· embedded systems
· integrated circuits
· digital-to-analog converters
· low-voltage differential signaling
7. Pulse generators
Pulse generators provide precise control over pulses — their sequence, timing, levels, pulse modulation, and duty cycles — for testing simple digital circuits, timing circuits, and related devices.
What are some key uses of signal generators?

We already listed a few high-level uses of signal generators in different industries but haven't been very specific. Below are some specific uses of signal generators for electronic testing and troubleshooting:
· Electronic test equipment: Signal generators are used for verification, calibration, and quality assurance of high-end test and measurement equipment like oscilloscopes and spectrum analyzers.
· Mobile communication systems: Microwave vector signal generators produce complex 5G and 6G signals with high signal purity for testing base stations and other elements of the radio access network.
· Aerospace: The complex digital signals used in avionics are tested using digital signal generators.
· Radars and defense: Radar transceivers are tested and qualified using microwave signal generators.
· Health care: Signal generators help ensure that medical equipment like magnetic resonance imagers and electrocardiographs have high signal-to-noise and common mode rejection ratios.
What are the key features and parameters to consider when selecting a signal generator?
When selecting a signal generator, you obviously need one that can produce all the typical waveforms that the device under test will see in operation. A signal generator's ability to produce complex realistic waveforms is influenced by some key specifications and features listed below:
· Waveforms: This is the variety of waveforms it's capable of. The most versatile capability for general-purpose applications is arbitrary waveform generation. However, for RF applications, other specifications matter more.
· Output power: This is the power of the generated signal and affects its range and accuracy. It's specified in decibel-milliwatts (dBm).
· Frequency range: This is the range of frequencies over which the generator can produce high-quality repeated continuous waves. It's specified in kHz, MHz, or GHz.
· Frequency switching speed: This is the time taken for the signal frequency to change on receiving a command. It's typically in the order of three milliseconds.
· Modulation: Which modulation formats does your use case need, and is the signal generator capable of producing them? Apart from basic schemes like frequency, phase, amplitude, and pulse, you must consider its capabilities for complex schemes like OFDM.
· Modulation bandwidth: This tells whether the generator can modulate over the full bandwidth of the baseband signal, which is essential to prevent any information loss.
· Phase noise: Phase noise is due to tiny, random fluctuations in the signal's phase that create instabilities around the carrier frequency. High phase noise restricts the ability to test high-performance receivers and also affects data integrity. It's specified in decibel-carrier per hertz (dBc/Hz) at different offsets from the carrier frequency. It gives the ratio of noise power to carrier power over a one hertz bandwidth at that offset.
· Spectral purity: Spectral purity is the inherent stability of a signal. It's specified using dBc, the ratio of the power in the signal's harmonics related to the power of the carrier signal.
· Sample rate: This is the rate at which the generator's digital-to-analog converter (DAC) produces discrete values of the continuous waveform. A higher sample rate enables higher frequencies, which is crucial for testing devices that operate at wide bandwidths. It also enables accurate representation of complex arbitrary waveforms.
· Real-time waveform generation: This is an advanced feature that enables complex digital modulation signals by interpreting the data bits and producing appropriate analog signals with the desired modulation.
How do signal generators work?
The working and internals of a simple function generator for analog signals are as follows:
1. Oscillator: This creates a stable frequency reference for the signal generation.
2. Waveform generator circuit: This produces the basic waveforms using analog techniques or based on a stored digital waveform.
3. Modulator: This applies the required modulation to the waveform.
4. Output conditioning: This consists of amplifiers and filtering circuits that amplify, filter, and match impedance before sending the signal to the output.
The more complex arbitrary waveform and vector signal generators use digital approaches like direct digitalsynthesis or Trueform. They first generate and manipulate a complex signal in digital form, apply digital signal processing, and finally convert it to an analog signal using a DAC.
Get the right signal generator you need for testing
This guide gave you an idea of signal generators, how they work, and their indispensability to electronics testing across verticals.
KEYSIGHT offers a wide range ofsignal generators for every use and industry:
· The VXG series of benchtop microwave vector signal generators with up to 110 GHz enable the advanced testing of 5G/6G mobile networks and non-terrestrial networks.
· The UXG series of agile vector signal generators enable the testing of electronic warfare equipment, radars, and antennas up to 44 GHz.
· The MXG, EXG, and CXG series are for common RF and microwave signal testing requirements in the 9 kHz to 40 GHz range.
The illustration below shows the frequency range of each product and should help you select the right one.
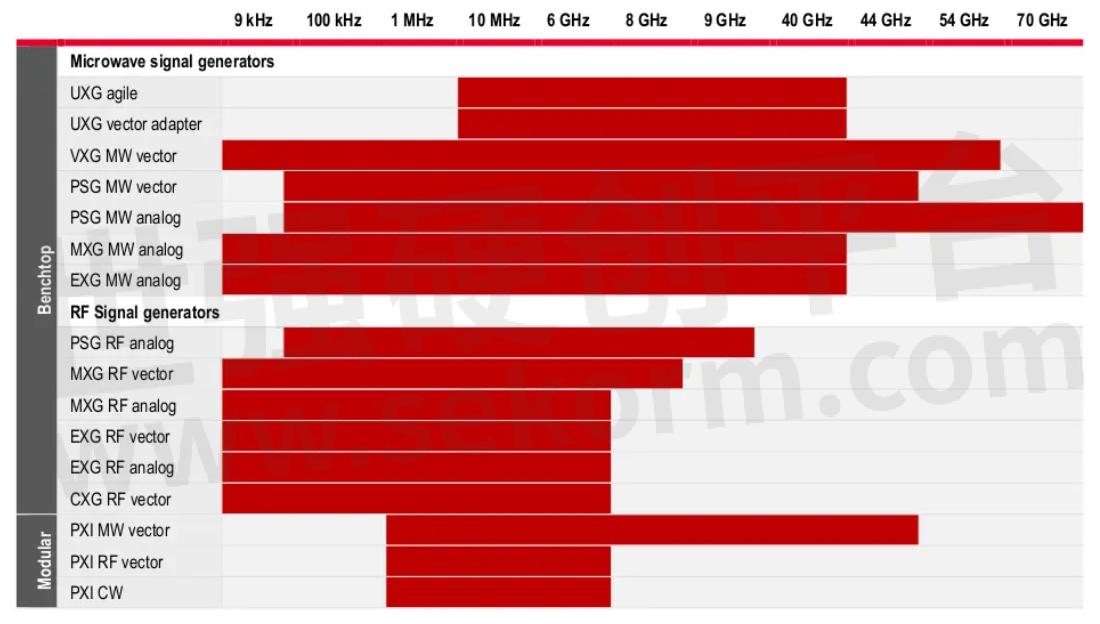
Fig 7. Frequency ranges of Keysight signal generators
We also offer calibration services for Keysight and several third-party signal generators.
- |
- +1 赞 0
- 收藏
- 评论 0
本文由出山转载自Keysight Blogs,原文标题为:Signal Generators: The Different Types and How They Work,本站所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源,不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
相关研发服务和供应服务
相关推荐
Signal Analysis in 5G NR Base Station Transmitters: Part 4
In this blog, Keysight discussed the 5G NR conformance test challenges and the latest industry signal analyzer (spectrum analyzer) solutions to overcome these testing challenges, and introduced its signal analysis solutions.
Learn the Basics of Signal Generator Accuracy
In this article, Keysight will provide guidance on the things you need to be aware of when selecting an RF signal generator.
安捷伦E4438C静电陀螺仪矢量信号发生器
型号- E4438C-401,E4438C-400,E4438C-422,E4438C-403,E4438C-SP1,E4438C-402,E4438C-259,E4438C-229,E4438C-407,E4438C-XXX,E4438C-409,E4438C-419,E4438C ESG,E4438C-250,E4438C-221
Keysight(是德科技)信号发生器选型指南(英文)
目录- Signal Generator Agile and Vector Signal Generators Analog Signal Generators Signal Studio Software PSG Signal Generators X-Series Signal Generators RF Analog Signal Generator Baseband Generator,Interface Module PXI Signal Generators Legacy Signal Generators
型号- 8657J,N5172B,E4425B,E4437B,8657D,8645A,8657B,8657A,ESG-D,8672A,N5173B,E4424B,E4436B,8644B,8656B,E4400B,E8257DSXX-SERIES,83620B,ESG-A,83620A,M9381A,8340B,8340A,N5106A,E4431B,8647A,N9310A,8648A,83712B,83712A,ESG-AP,E4430B,83752B,83752A,M9380A,83630L,N5191A,8662B,E8257D,8662A,E4438C,E4426B,E2500B,83711B,83711A,83630B,83751B,83751A,8665A,8665B,E4421B,E4433B,N5193A,83640L,N5181B,8341A,N5181A,8341B,E8663D,8664A,E4428C,E4420B,8648D,E4432B,8648B,E8267D,8648C,83624B,83624A,83640B,N5194A,8780A,N5182B,N5182A,83623L,E4435B,8643A,N5102A,E4423B,83732B,83623B,83732A,83650L,N5171B,N5183B,8763D,N5183A,8763B,8763C,E8257DVXX-SERIES,X-SERIES,8763A,E4422B,E4434B,83622B,83731A,ESG-DP,83622A,83650B,83731B
M9484C VXG和V3080A矢量信号发生器和频率扩展器数据表
型号- M9484C-508,V3080A-F06,M9484C-506,V3080A-F07,M9484C-514,M9484C-544,M9484C-532,M9484C-554,M9484C-520,M9484C VXG,V3080A-F09,V3080A,V3080A-F11
MXG X系列信号发生器N5183B微波模拟数据表
型号- N5183B-513,836XX SERIES,E8244A,8665A,8665B,SMJ100A,8648,N5183B-520,8648 SERIES,SMIQ,N5181A,N5161A,8341B,E8267C,E8247C,SMBV100A,E4428C,E443XB,8664A,E8251A,8656B,8644A,E8663B,E8267D,SML,SMR,SMATE200A,SMV,N5162A,N5183B-532,SMU200A,N5182A,8340B,E8254A,8663A,83732B,MXG X,83712B,SMB100A,83752B,N5183B-540,E442XB,N5183B,N5183A,SMF100A,E8257D,E8257C,8662A,X-SERIES,E4438C,E8241A,MXG X-SERIES,83711B,MG369XA,836XX,MG369XB,MG369XC,83751B,83731B
E8257D PSG微波模拟信号发生器数据表
型号- E8257D-UNY,E8257D-1EU,E8257D-UK6,E8257D-UNX,E8257D-UNW,E8257D-UNU,E8257D-UNT,E8257D-AMG,E8257D-HCC,E8257D-550,E8257D-1ED,E8257D-C09,E8257D-1SM,E8257D-H1S,E8257D-1EM,E8257D-513,E8257D-532,E8257D-1EH,E8257D-A6J,E8257D-HY2,E8257D-ABA,E8257D-1E1,E8257D,E8257D-1A7,E8257D-540,E8257D-008,E8257D-567,E8257D-007,E8257D-521,E8257D-520
MXG X系列信号发生器N5183B微波模拟配置指南
描述- 本资料为MXG X-Series微波模拟信号发生器N5183B的配置指南,详细介绍了如何根据需求选择频率范围、连接器配置、性能增强选项、软件应用、附件和售后服务等。指南还包括了如何升级现有MXG信号发生器的信息,以及相关文献和联系方式。
型号- N5183B-1ED,E8257D-V08,N5183BU-UW2,E8257D-V06,E8257D-V05,PS-X10,N5172B,N5183B-513,N5183B-1EM,N5183B-AMG,N5183A-1ED,N5183B-1ER,N5183A-HNS,N5183A-1EA,N5183A-540,E8257D-V03,E8257D-V02,E8257D-V01,N5183B-UZ2,N5183A-1E1,N5183BU-006,N5183A-UNZ,N5183B-520,N5181B,N5183B-006,E8257D-V15,N5183BU-UZ2,N5173B,E8257D-V1B,PS-T10-ASG,PS-S20,N5183B-CVR,N5183A-532,1CM110A,N5183BU-1ER,N5183A-UNT,N5183B-UNC,E8257D-V12,E8257D-V10,N5183A-UNW,N5183B-UW2,R-50C-011-10,PS-S10,N5183B-532,N5183B-A6J,N5182B,N5180320B,N5183BU-1EA,N5183B-UNT,E8257D-V2B,N5183B-UNW,1CN106A,N5183BU-0BW,1CR112A,N5183A-520,N5183B-UNY,N5183B-UK6,N5183B-UNZ,N5173BU-1E1,N5183BU-AXT,N5183A-006,N5183BU-303,N5183B-CD1,N5183B-540,N5183BU-CD1,N5171B,N5183B,N5183B-303,X-SERIES,R-50C-011-5,N5183B-1E1,N5183B-AXT,R-50C-011-7,N5183A-HNZ,N5183BU-UNZ,N5183BU-UK6,N5183B-0BW,N5183BU-UNW,N5183BU-UNT,N5183A-1EM,N5183B-1EA,1CM104A,N5183A-1ER
SCPI命令参考卷3安捷伦科技E4428C/38C ESG信号发生器
型号- 8648A,8657J,E44XXB,E4438C,8657D,E4428C,8648D,8657B,8648B,8648C,8658B,8657A
Simplify Complex RF Testing with Vector Signal Generators
As the number of antennas in a system has increased, so has the test complexity. So, Keysight shares the way to Simplify Complex RF Testing with Vector Signal Generators M9484C.
N5181A MXG模拟N5182A MXG矢量第一代MXG信号发生器
描述- 本资料为Keysight Technologies公司第一代MXG信号发生器的配置指南,包括MXG模拟和矢量信号发生器。指南详细介绍了订购过程,包括选择型号、频率选项、性能增强选项、输入/输出选项、附件和文档选项、校准选项和启动辅助服务选项。同时,资料还提供了升级至新一代EXG信号发生器的信息,以及可用的选项和升级内容。
型号- N5182AK-432,N5182AK-430,N5182AK-672,N5182AK-431,N5172B,N5182AK-670,N5171BU-1EA,N5182AK-671,1CP004A,N5172B-UNV,N5182AK-1EQ,N5182AK-1ER,N5172B-UNW,N5172B-UNT,N7622A,N5182AK-1EL,N5182A-UNW,N5181AK-UNZ,N5172B-OBW,N5171B-320,1CM010A,N5172B-UNZ,N7606B,N5182AK-1EA,N5172B-320,N5182AK-320,N5181A-AXT,N5161A,N5181A-CD1,N5181AK-UNT,N5171BU-320,PS-S20,N5181AK-UNU,N7621B,N5181AK-UNW,N7617B,N5171BU-1ER,N5171B-1EM,N5171B-1ER,N5182AK-654,N5181AK-320,N5182AK-652,N5182AK-012,N5182AK-651,N5171B-0BW,N5182AK-099,N7624B,N5171BU-099,N5172BU-021,N5171B-1EA,N7612B,N7600B,N5182AK-019,N5171BU-006,N5172BU-655,N5182AK-250,UK6,R-50C-011-3,N5172B-CD1,N5172B-AXT,N5172BU-653,N5182A-0BW,N5172BU-012,R-50C-011-5,N5172BU-099,N5181AK-1EQ,N5172B-503,N5181AK-1ER,N5172B-506,N7623B,N5182AK-ALB,N7611B,1CR012A,N5171B-099,N5172BU-22X,N5181AK-0BW,N5172BU-403,N5172BU-006,N5181AK-1EA,N5172B-653,N5172B-655,N5181A-1CM,N5172B-012,N5181A-1CN,N5172B-099,PS-X10,N5181A-1CP,N5181AK-ALB,N5182A-AKT,N7602B,N5172BU-320,N5182A-1CR,N5182A-1CN,N5181A-AKT,N5182A-1CP,N5172BU-1EL,N5182A-1CM,N5171B-006,N5172BU-25X,N5181A-1CR,N5172B-021,AMG,N5172BU-1ER,N5181AK-099,N5182AK-006,N5172B-403,N5172B-006,N5182A-ABJ,N5181A,N7613A,N7625B,R-50C-016-5,N5172BU-432,N5172BU-431,PS-T10-ASG,N5172BU-430,N5182A-ABA,N7601B,N5182AK-403,N5172BU-1EA,N5182AK-R2C,N5182A-AB2,N5182A-AB1,R-50C-021-5,PS-S10,N5172B-430,N5182A,N5181AK-006,N5172B-432,N5172B-431,N5182AK-UNW,N5182AK-UNV,N7616B,N5182AK-UNU,N5172B-1ER,N5182AK-UNT,N5172B-1EM,N5172B-1EL,N5171B-CD1,N5172BU-UNT,PA-T10-ASG,A6J,N5171B-501,N5171B-503,N5172BU-UNZ,N5171B-506,N5171B-AXT,N5172BU-UNW,N5172BU-UNV,1CN006A,N5171B-UNZ,N5182AK-221,N5172B-022,N5181A-AB1,X-SERIES,N5181A-AB2,N7615B,N5182A-AXT,N5172B-0BW,N5181A-ABJ,N5171BU-UNT,N5182AK-UNZ,N5172B-1EA,N5181A-ABA,N5171BU-UNW,N5171BU-UNZ,N5171B-UNT,N5182A-CD1,N5171B-UNW
E8267D PSG矢量信号发生器数据表
型号- E8267D-1A7,E8267D-HFA,E8267D-H1G,E8267D-409,E8267D-009,E8267D-544,E8267D-423,E8267D-SP2,E8267D-602,E8267D-007,E8267D-403,E8267D-004,E8267D-SP1,E8267D-520,E8267D-003,E8267D-H18,E8267D-HCC,E8267D-UNW,E8267D-UNY,E8267D-UK6,E8267D-UNX,E8267D-1EM,E8267D-UNU,E8267D,E8267D-UNT,E8267D-AMG,E8267D-016,E8267D-A6J,E8267D-HBR,E8267D-513,E8267D-HBQ,E8267D-532,E8267D-1EH,E8267D-HNS,E8267D-1ED,E8267D-H1S
现货市场
服务
整体外形尺寸小至0.6*0.3*0.3mm (DFN0603),工作电压范围覆盖2.5V~36V,电容值低至0.2pF,浪涌能力最高可达240安培,静电等级可达空气放电、接触放电±30KV。提供免费浪涌测试仪、静电测试仪测试。
提交需求>






























































































































































































登录 | 立即注册
提交评论