Understanding the RF power in a coaxial cable assembly




One of the most often asked questions from our customers about our cable assemblies is “How much power can this cable assembly handle”. My response is usually the same, “It depends”. This question cannot be understood in its completeness without the understanding of power, and the many variables that contribute to the makeup of power transmission. This white paper will serve to shed some light on this issue, and at the same time, give some practical examples seen in the industry. In addition, hopefully, it will explain why it is difficult to just give a chart or table for all of our cable assemblies with regard to power handling.
Why do we need RF Power transmission? In Radar, for example, we transmit high power in order for the signal to be sent at a great distance. Any cable attached to this antenna must be able to handle the same power and thus must be carefully chosen.
Power fundamentally is Energy transferred per unit of Time. A Power amplifier sending energy down a transmission line “transfers” this energy from point A, to point B. You will find a couple of different ways to express power such as “Watts” or “Milliwatts” (mW), as seen in the power amplifier world, or it can be expressed in dBm, (decibels per milliwatt), as we see in the Telecom world.
The basic conversions from one to the other can be seen below:
dBm = 10 Log10 P (milliwatts)
P (milliwatts) = 10 (dBm/10)
For example, the +43dBm signal would be then equal to 19,952 milliwatts or about 20 watts. And a VNA output power of 100 mW is about 20 dBm.
Operating power is important, however, there are other factors needed to determine what cable assembly will fit a certain application. Before discussing this, we need to first look at another important factor of power, and that is Peak Power vs. Average Power.
Peak Power can be defined as that power where what is called the “Voltage Gradient” is at its maximum. In other words, we have in the coaxial cable a potential between the inner conductor and outer conductor. When this potential becomes too large, the voltage will want to jump from the inner to the outer conductor bypassing the insulator medium (Air or PTFE, or other insulation materials). When this “jump” in voltage happens, the voltage gradient is at its maximum. So then Peak Power in a cable assembly is limited by the Voltage Gradient. This is the reason we must pay attention to the “Operating Voltage” of an assembly. The operating voltage is normally set in order not to exceed this voltage gradient. This is one of the main reasons we perform Dielectric Withstanding Voltage (DWV) tests on our assemblies which essentially verify if this voltage gradient is exceeded. Steps need to be taken in connector design, as well as the connector to the cable assembly process, to ensure success.
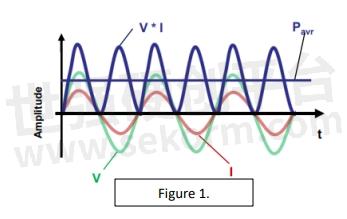
Next, we have Average Power. Once we get passed the limit of Peak Power due to the voltage gradient, we turn to Average Power and concern for dissipating heat. Most of our RF signals are either sinusoidal or pulsed in nature. Figure 1. is an example of a sinusoidal power wave. Average power, also known as Continuous Wave or “CW” power, is what we base most of our calculations on when answering application questions on power handling. Even when the signal is a pulsed square wave as we find in radar applications, this can be reduced to average power by multiplying the Peak power by the duty cycle. For example, a 500 W peak signal with a 10% duty cycle, equates to a 50W average power signal.
So, what are these variables that affect power in our cables as mentioned earlier? The first one is Frequency. The main premise being as the frequency increases, the power decreases. The simple reason is that due to the laws of Microwave Signal Transmission, higher frequencies are supported and transmitted in smaller cables, and the smaller the cable, the harder to dissipate the heat resulting in power loss.
The second variable is VSWR. Reflections caused by mismatches in impedance will also account for power losses in a cable assembly. At any point on a transmission line where the impedance doesn’t match the characteristic impedance, you will have a mismatch, and therefore VSWR (or Return Loss). Since part of the power signal was “returned”, we have power loss.
The third variable is Altitude. Normally when power figures are given for a particular assembly, you might see a qualifier such as “Sea Level”. The reason is that power for a cable is different at Sea Level than say at 70k ft. So, we need to derate a cable for altitude. The reason is due to the air molecules. Air molecules are excellent in removing heat away from hot objects. The higher in altitude, the less air molecules, so we need to account for this in our power ratings. The below chart in Figure 2. displays the derating factor at different altitudes. Simply put, if you have a cable that can handle 50 watts at Sea Level, then that same cable can only handle 14.5 watts at 70,000 feet.

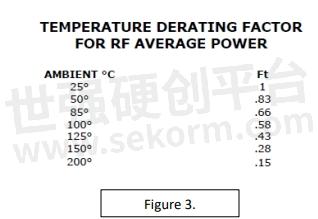
The final variable in the Power transmission equation is Temperature. This was alluded to before regarding cable size and the ability to dissipate heat. However, we also have the environment around the assembly to consider, and this will affect the performance of power. The high current in the center conductors increases the temperature rather quickly. Copper is a common conductor material, great for conducting electrical signals as we as heat. This heat needs to dissipate from the assembly to maintain its current power level. If the environment outside the assembly is at a high temperature, then this dissipation is slower or not possible at all. Because of this, we need also to derate an assembly with respect to temperature (see Figure 3.).
How then do we calculate the power handling capability of our cable assemblies? First, we need to know the power requirement (average or CW), frequency, temperature, and altitude of the application. Next, the connectors need to be identified. With this information, an average power figure can be calculated.
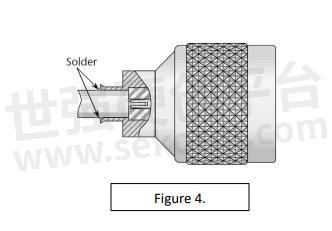
We need to understand that the cable assembly is made up of cables and connectors. The power possible in the assembly is dependent on both the cable and connectors, and either can be the weakest link. It is also worth noting that the cable/connector junction can often be the point of lowest power transmission (see Figure 4.).
The two examples below will illustrate the issue of connector vs. cable. The first example is a Type N connector mounted on a .047 s/r cable operating at 6 GHz. In this example, the connector can handle about 1200 W at sea level and 25 deg C. The cable on the other hand, can only handle about 21 W. So, a cable assembly with this criterion must start at 21 watts when considering power. The second example is an SMA connector mounted on our Lab-Flex 290 cable. At the same frequency of 6 GHz, the power capability of the SMA is about 150 watts, with the power capability of the 290 cable at about 1800 watts. Therefore, we can’t just look at the power capability of the cable, as it might not be the weakest part of the equation. These two examples are the two extremes of what can happen. Keep in mind as mentioned before that the cable/connector junction in Figure 4. may also be the weakest link. In addition, if the assembly is to be used at a higher altitude or temperature, it needs to be derated as noted above.
One final thought about connector interfaces, and how they relate to power. There are some connectors that can reach a higher power rating than others. This has to do with the construction of the interface. Remember the discussion above regarding the voltage gradient. Interfaces typically are designed with PTFE or Air or a combination of the two. These materials will dictate how much power the interface can handle. This voltage gradient is related to the “dielectric strength” of a material. It so happens that the dielectric strength of air is 70 volts/mil, and for PTFE it's 1000 volts/mil. This means that for an air interface, every .001” gap between two metal surfaces, you can have a potential of 70 volts, above which you will reach a maximum voltage gradient. PTFE has a dielectric strength of much greater magnitude. This is generally why a standard TNC interface can handle much more power than an SMA interface. See Figure 5. & Figure 6.

You can see by the two interfaces above that there is a much shorter path from the center conductor to the outer conductor in the SMA design, than in the TNC design. In addition, the TNC design has insulators that fit one inside the other. This increases the conductive path from the center conductor to the outer conductor and therefore increases the power capability.
So, in summary, the power capability of a coaxial cable assembly is dependent on the voltage gradient throughout the assembly. The average power of an assembly can be computed readily if the frequency, altitude, and temperature are known, and the VSWR is approximated. We must understand the power capabilities of both the connectors and the cable to get the full picture. Lastly, interface design is key to higher power operation with PTFE being a better interface material especially if it’s a telescoping type design seen in Figure 5.
The above information should shed some light on the difficulty of just displaying a chart or graph of all the different power possibilities for our cables. If such power information is needed, please forward the details of your application to us, and we will be quick to respond with your information.
- |
- +1 赞 0
- 收藏
- 评论 0
本文由涂抹转载自Smiths Interconnect Blogs,原文标题为:Understanding the RF power in a coaxial cable assembly,本站所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源,不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
相关推荐
Smiths Interconnect is Transforming New Product Development with “CAD-to-FAB“
‘CAD-to-FAB’ - CAD stands for ‘computer-aided design’ and FAB for ‘digitised fabrication.’ Combined, this process can streamline and clean up the entire production line, from concept to customer-ready unit.
Equalizing the Slope Gain in Your Next RF&Microwave Design, Smiths Interconnect Support the Trends and Technology of the Future
When looking at key design trends for RF & microwave components such as higher frequency, increased bandwidth, and larger component counts, it becomes apparent that RF/microwave engineers will have to look for new ways to deal with inherent challenges in gain slope that are exhibited by many RF components.
Smiths Interconnect 微波元器件 选型指南
描述- Smiths Interconnect is a leading provider of technically differentiated electronic components, subsystems, microwave and radio frequency products that connect, protect and control critical applications in the Defence and Aerospace, Communications and Industrial markets.
型号- 82 7013TC,32 1209,83 7017TC,33 1052,HPR2F,D3PP20F,CR0402D,33 1050,DS15D10,42WXX.00F,SMT2010TALN,32 1200,82 3003TC,32 1201,81 7042,32P7201F,31 7021,81 3012B,KTVA SERIES,HE298MF,12-0101,12-0102,13-125-T,82 7001TC,81 7021TC,83 7006TC,33 1041,4113P,33 1042,QTVA,8485 SERIES,82 3038TC,32 1212,SMT2010*A,42UW SERIES,32 1213,81 3001B,81 3001A,81 3033TC,42TVA,CR1010D50,5W2,SXUXXXX3F,DS15D20,SMT3737*ALN,CA0505D T,4112P,42KA,P2D50J,DN05W20F,811,812,49XX,83 1001TC,4111P,SD055-055-4-A,82 7025TC,SD055-055-4-B,SD065-035-3-B,5654 XXX,5,TS0710S,82 3039TC,CR1010D50,5TB,81 7031,32 1111,32 1117,81 3011B,81 3011A,5308 XXX,5,81 7028,31 7008,31 7006,5660 XXX,5,32-7172F,823,827,82 7002TC,HPP2F,HN05W03F,HRM,32 1002,32 1123,32 1121,HRT,SD130-105-4-040,83 3005TC,32 1001,32 1122,D3PPXXF,32 1006,32 1007,32 1004,82 7166TC,82 3001TC,32 1005,81 3001TC,CT3725,33 1009,33 1005,33 1006,33 1003,12-250-T,CA0505DXXFT,33 1004,SMT2010*ALN,CT2335TALN,4110J,33 1001,33 1002,SD055-055-3-B,SD065-035-4-A,32P7204F,SD065-035-4-B,83 8999,HRTVA,83 3016TC,TVA SERIES,32 1014,81 3035TC,HR03,32 1138,32 1017,HR05,32 1137,81 3012TC,CT1310D,11-125-T,32 SERIES,D2PL05F,841X SERIES,CT3737,841,842,843,HD064M3F,83-7027-10.00F,846,CT2525,AN7 SERIES,83 7999,ETVA SERIES,12-250-TP,83 3006TC,QFA,32 1026,CT3725_ALNS,CT1206,AN11 SERIES,CT3737TALN,33 1021,TS07,TS06,83 1003TC,TS05,TS04,TS03,CT2335*ALN,5653,42TVA SERIES,32 1035,32 1156,81 3034TC,32 1036,32 1157,32 1034,DN15D10F,32 1039,32 1158,32 1037,TS09,CT0505DT,32 1160,WH0825F,CA0505D,32 1161,32 1041,32 1162,QTVA03N0SMTF,SXXXX-XXX-X-XXX,33 1017,81 7043TC,CR0402D SERIES,QFAXX0XSMTF,81 3008B,TS0620F,31AZ021-050-5F,81 3003TC,CT0505D SERIES,82 7187TC,81-Z008TC-100-5F,SD055-055-4-015,8482 SERIES,32 7037,83 3994TC,875,HRMTVA,D2PLXXF,5657,5659,CR0603D,SD065-035-4-025,CT2010*A,SMT3725,QTVA SERIES,81 7108TC,82 3019TC,5 SERIES,CT3725F,82 7176TC,CT0505DTB,83 3999,32 7163,12-5061,SD045-025-4-A,83 3998,32 7164,SD045-025-4-B,32 7165,SD050-020-3-B,83 3995,CA0505D FT,5307,843X SERIES,CT1206*ALN,AN5 SERIES,81 3006A,82 3008TC,CR0505D,5323,HR0520AW3S,81 3006B,SXU15203F,83 1996TC,81 3002TC,823X SERIES,82 3213TC,SD120-080-5-A,XPDF,31 1099,12-5050,31 1098,12-5051,32 7176,32 7172,8488 SERIES,81 7109TC,CT1005TALN,XFMRF,MTVA0300N05W3S,SXU00203F,SD105-105-4-035,811X SERIES,12-5042,SD045-025-3-B,32 7187,12-5049,81 3123TC,73-0160-100,5310 XXX,5,82 3005TC,12-5032,81 3036,WTVA0300N05SMTF,SMT252503ALN2F,32 7196,42S,81 3032,81 3031,42W,82 7030TC,TS0410S,32 7195,SXU20103TF,83 7011TC,83 7034TC,SMT2525*A,TS0910SMTF,32 7191,81 3039,AN3,AN5,CR040W2 SERIES,AN7,81 3005B,81 3005A,31 7110,83 1006TC,CT0505,12-5021,812X SERIES,31 7109,CR040W2,31 7108,41 SERIES,XPMRF,31 7107,11-250-TP,12-5029,42UW,81 7008TC,12-5028,83 7023TC,SMT2525*ALN,CT1005*A,P4L35G,AN SERIES,8750,82 3006TC,82 3029TC,81 3027TC,81 3002A,HPK2F,82 7163TC,D3MDXXF,D15D20,COAX TVA,81A7042_-100-5F,83 3997TC,12-5014,12-5012,12-5013,CT3725*ALN,81 3003B,81 3003A,81 7107TC,842X SERIES,KTVA,12-5007,42S SERIES,12-5005,CT0402,KTVA0300N052F,8750 SERIES,TVA,HR0320AW3S,81 3028,D2PK02F,81 7001B,D3PV30F,32P7196F,HRM030AN05W3S,AN5-XNXF,SMT1206 *ALN,31 1033,31 1035,31 1034,31A7021-050-5F,P3S35J,P3S35L,8487 SERIES,RPD0212F,TRP 4-12,82 7172TC,SMT3725*ALN,82 3030TC,12 SERIES,41XXPCD,SD105-105-4-A,8XXX,SD105-105-4-B,81 7006TC,81 3006TC,SMT3737*A,WTVA SERIES,KFA,SMT SERIES,KFAXX.00-5SMTF,31 1010,841X,D2PJXXF,TRM4-12_XXX,5,33 7023,CTVA0300N05W3F,5326 XXX,5,83 SERIES,83 7044,WTVA,83 7046,83 7047,SMT3725*A,DN05Z15F,82 7150TC,82 3031TC,HPCA5410.00W3S,SXU10203TF,827X SERIES,31 1021,42 SERIES,842X,CT0402D,SMT3725TALN,42TVA0300N05F,HE128MF,12-3022,42,CR1010D,4112PLC,HLB2F,31 1086,SXU00303F,CT0603D SERIES,33-7XXX-XX.XXF,31 1076,33 7002,843X,33 7001,33 7004,CR0603D SERIES,33 7005,D2PJ30F,12-3007,P4L50G,31 1094,TRM 4-12,5318 XXX,5,82 3051TC,MTVA,31 1089,82A7176TCF,HPX2F,SMT372501AIN2MF,BD064M3F,12-3005,P2S35D,CT0505D,12-3002,SD045-025-4-015,12-3001,SMT3737,81 3008TC,SMT2525,CTVA,846X,D2DL20F,32P7198F,HRTVA SERIES,83 3021TC,D3PVXXF,HPG2F,42KA SERIES,82 3040TC,31 1059,32-1003,31 1054,83 8054,CT1310D SERIES,8487,8485,823X,8488,TRP 6-12,32P7197F,31 1075,12-125-T,31 1074,8482,TRP 6-18,SXU15303F,846X SERIES,81AZ042-100-5F,32 7024,32 7025,CT2525*ALN,32 7027,13-250-T,5653ALN,32 7023,TVA0300N05W3S,5318XXX5,42W SERIES,CT0402D SERIES,82 7017TC,812X,XPRF,5309L,32 1046,32 1047,32 1168,HPD2TF,82 3045TC,HD128M3F,CTVA SERIES,32 1050,AN11,32 1051,SD130-105-3-B,CT2335*A,811X,81-SERIES,4111PCD,82 7005TC,13-125-TP,TS0320W1S,11-250-T,32 1055,CR0505DT2,SMT372503ALN2F,TRM 8-18,81 3075TC,CR0505D SERIES,32 1184,D3FUXXF,CR0505DTB,81 3002BV,HPCA,32 1068,HDC2F,82 3023TC,HE450M2F,CT2525TALN,5307ALN,33 700,32 1070,32 1191,SD130-105-4-B,32 1196,SD130-105-4-A,32 1074,HG064M2F,82 SERIES,CT0603D,RPDXXXXF,CT1005,CT2335,HRMTVA SERIES,827X,RPD0412F,CR0402D W2,82 3209TC,KTVA0300N055SMTF,83 7009TC,82 7192TE,32 1198,32 1199,82 3012TC,81 3074TC,32M7200,12-0001SF,4915,CA0505DXX,32P7197,HRT030AN05W3S,4910,HDS2F,TS0520W1S,83 7014,ETVA0300N05S,82 7015TC,81-7008TC-1005F,RPD0312F,
Smiths Interconnect 线缆组件选型指南
目录- Company and product introduction Cable Semi-Rigid/Conformable/Flexible Cable Semi-Rigid Low Loss Cable MIL-C-17/RG Series Cable LMR Cable Cable Assembly Options Cable Application Notes Cable Engineering Data Introduction
型号- RG405,402TP,RG401,LMR-240,RD316,RG402,405TP,SMS-RG142_-18.0-SMS±2.8PS,LMR-240-LLPL,LMR-400,250TP,LMR-400-LLPL,AL250LLTP,LMR-400-UF,LMR-100A-PVC,SF316,LMR-240-DB,AL141LLSP,BJ085,LMR-400-DB,142D,BJ141,LMR-195,RG316,KMS-AL141LLSP_-12.0-KMS±2.8PS,SF 142,LMR-240-UF,AL141TP,BJ047,SMS-BJ085-18.0-SMR±2.8PS,SMS_100_24.0-SMS_,AL085TP,RG223,316D,RG400,AL085LLSP,RG142
Lab-Flex®T系列相位测试同轴电缆组件
描述- Smiths Interconnect的Lab-Flex® T系列同轴电缆组件专为雷达和测试应用设计,提供高频率和宽温度范围内的稳定电气性能。该系列电缆组件采用特殊泡沫氟聚合物绝缘材料,以最小化温度变化引起的相位偏差,适用于商业和军事市场。产品经过严格测试,确保满足客户和行业标准。主要特点包括相位匹配对和集、温度稳定性、低损耗等。
型号- LAB-FLEX® T,065T,LAB-FLEX® 100T,100T,LAB-FLEX® 160T,LAB-FLEX® T SERIES,LAB-FLEX® 065T,160T
Lab-Flex®系列高性能同轴电缆组件
描述- Smiths Interconnect的Lab-Flex系列产品提供高性能同轴电缆组件,适用于多种应用和市场。该系列以其可重复、一致的性能和高可靠性而著称,有助于降低拥有成本并提高系统性能。Lab-Flex电缆具有低损耗PTFE绝缘体和镀银铜中心导体,适用于卫星通信、雷达、导弹制导和测试测量等领域。
型号- 200,LAB-FLEX SERIES,125,LAB-FLEX® SERIES,LAB-FLEX,190,LAB-FLEX®,290,160
Phase stable Cable Assemblies: Reliability Where It’s Needed Most
When it comes to cable assemblies, Smiths Interconnect specializes in MIL-STD-348 RF connectors. These devices are typically used in defense, space, and testing applications for the transmission of RF signals used for communication and information transmission.
SpaceNXT™QT系列空间合格相位稳定同轴电缆组件
描述- Smiths Interconnect推出的SpaceNXT™ QT系列太空合格相稳定同轴电缆组件,适用于太空环境,具有优异的相位稳定性和辐射抗性,满足NASA/ESA的放气规格。该系列电缆适用于卫星通信、导航、军事、商业和科学项目,以及GEO/MEO/LEO和微小卫星平台。
型号- 160QT,QT SERIES,100QT,065QT
半刚性电缆间隔合格电缆组件
描述- Smiths Interconnect提供的半刚性电缆组件适用于卫星有效载荷(地球同步轨道/中地球轨道和低地球轨道星座)、深空探测器、地面天线网络、卫星集成和太空机器人系统。这些电缆具有高性能、可靠的介电特性和优异的屏蔽质量,经过空间轨道认证。它们可根据客户规格提供直形或预弯曲,并带有铜或铝护套以及多种镀层和四种不同直径(0.047英寸、0.085英寸、0.141英寸和0.250英寸)。高频率(高达65 GHz)、低插入损耗、卓越的屏蔽效果、现场认证和历史经验使这些电缆成为在关键系统中实现出色电气性能的理想选择。
238500-8017塑料光纤终端/电缆组件
描述- 本资料介绍了Smiths Interconnect提供的用于#16 MIL-DTL-38999连接器的塑料光纤(POF)端子和电缆组件。这些组件具有易于终止、成本低、重量轻、抗干扰等特点,适用于多种应用。
型号- 238400-8011,238500-8017
Smiths Interconnect Micro-D Twinax连接器选型指南
目录- Micro-D Twinax Connectors Micro-D Twinax Connectors
型号- 014117-0014,014117-0016,014117-0012,014034-0012,014134-0016,014034-0014,014134-0014,014034-0016,014034-0018,014134-0018,014134-0012,540-1167-000,018934-0003,018834-0002,018934-0002,018834-0003,018834-0004,018934-0004,014117-0018,014117-1114,014117-1116,014117-1112,540-1153-000,540-1161-000,014117-1118
商业航空航天连接解决方案
描述- Smiths Interconnect 是商业航空航天领域高可靠性连接产品和服务的主要供应商。公司提供高性能连接器解决方案、天线系统、射频组件和电缆组装,服务于飞行控制与导航系统、发动机系统、电源分配、卫星通信连接等多种航空应用。其技术品牌包括 EMC、Hypertac、IDI 等,专注于为高科技、高质量解决方案提供卓越性能,以满足高度安全和耐用性需求。此外,Smiths Interconnect 还提供广泛的认证标准和技术支持服务,以适应全球市场。
测试电缆组件和同轴无源元件DC-65GHz
描述- 该资料详细介绍了Florida RF Labs公司提供的多种高性能测试电缆和同轴无源组件。包括Lab-Flex®系列电缆,涵盖不同频率和接口类型,如SMA、2.9mm、Type N等,适用于不同测试应用。此外,还介绍了Titan-Flex™、Mini-Flex、Pro-Form™等电缆,以及同轴终端和衰减器等无源组件,适用于DC至40GHz的频率范围。资料还提供了电缆性能参数、接口类型和编号代码等信息。
电缆组件线束连接器IRIS认证®:ISO/TS 22163:2017(1211360277)
描述- Hypertac GmbH获得TÜV SÜD Management Service GmbH颁发的IRIS Certification®认证,确认其管理体系符合ISO/TS 22163:2017标准,涉及设计和开发、制造活动。证书有效期为2022年1月14日至2023年2月21日,包括电缆组件、连接器和定制互连解决方案的设计、开发、制造、组装、测试和销售。此外,公司在法国Saint-Aubin-Les Elbeuf设有远程地点,也获得了相应的设计与开发及项目管理证书。
铁路连接解决方案
描述- Smiths Interconnect作为铁路连接解决方案的供应商,提供安全、高效、可靠的连接产品。公司拥有60多年的经验,提供高性能连接器、天线系统、射频组件和电缆组件。产品涵盖防务与航天、通信和工业市场,包括高可靠性电气连接器和电缆组件、坚固嵌入式收发器、天线系统解决方案以及广泛的创新射频和微波解决方案。公司注重可持续发展,产品符合主要国际铁路标准,并提供全球范围内的技术支持和本地服务。
型号- HDC SERIES,HBB SERIES,C SERIES,BOA SERIES,L SERIES,B SERIES,M12 SERIES,F SERIES,H/N SERIES,LHS SERIES,CEA SERIES,LHZ SERIES,REP SERIES
电子商城
品牌:Smiths Interconnect
品类:TEMPERATURE VARIABLE CHIP ATTENUATOR
价格:¥37.0712
现货: 3,100
品牌:Smiths Interconnect
品类:TEMP VARIABLE ATTENUATOR
价格:¥11.5897
现货: 2,677


































































































































































































登录 | 立即注册
提交评论