What is Error Detection Correction, LDPC, BCH, Reed-Solomon Algorithm?




Error Detection and Correction in NAND Flash Memory
The current age of information underscores the need, not only of speed but also of accuracy, whether one is storing, retrieving, transmitting or analyzing data. Considering the amount of critical information being generated by the minute, even the slightest of errors can spell disaster. As flash memory moves to smaller geometries, error bits also increase, requiring more powerful error correction algorithms to ensure the reliability of the flash storage device.
Bad Blocks
Bad blocks are blocks that have one or more invalid bits. They may be unusable or weak and prone to errors. They may be present even in new devices and may develop during the lifetime of the device.
There are two types of bad blocks in a NAND flash storage device:
Initial bad blocks. NAND flash devices may ship out with a number of bad blocks. Before the device is shipped, the location of bad blocks is mapped, and a bad block management algorithm is usually implemented, where a bad block table is created by reading all the spare areas in the flash storage device. Invalid blocks are identified during testing and validation in the factory. The bad block table is saved in a good block, so it can be loaded by the device on reboot (Micron).
Accumulated or Later Bad Blocks. As the device goes through the rigors of its use, data in the good blocks may be lost or corrupted due to wear out during its lifetime, leading to read/write disturb errors, retention errors, and other issues. Consequently, damaged blocks cause stored data to be inaccessible and applications or operating systems may fail to open. As bad blocks increase, drive capacity decreases and performance is compromised, eventually resulting in device failure.
NAND Flash Degradation and Bit Errors
Error correction codes are employed to detect and correct bit errors. In the early days of flash, single-digit error codes were used, but as scaling became prevalent, cell size decreased and bits per cell increased. The following factors impact flash degradation and the rise of bit errors.
Program/Erase (P/E) Cycles. The constant cycles of programming (writing) and erasing require the application of high voltage to the NAND cell, causing stress on and weakening the Tunnel Oxide.
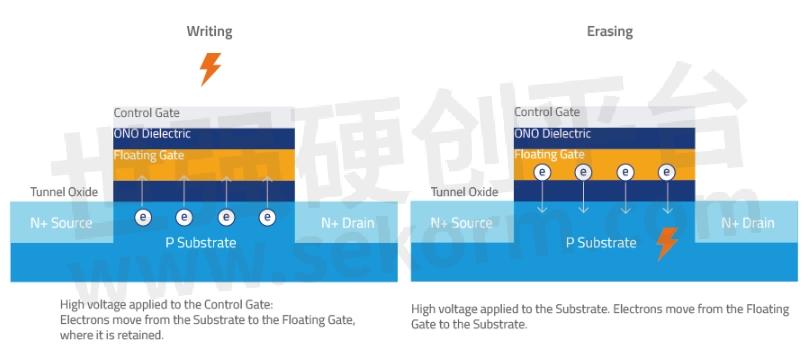
Figure 1. Program (write) and erase operations on the NAND flash cell require the application of high voltage, which causes stress on the Tunnel Oxide. As P/E cycles increase, the Tunnel Oxide weakens, causing electrons to leak out from the Floating Gate and the NAND flash cell to degrade.
More bits per cell. In efforts to increase density, new flash technologies have enabled the storing of more bits in a cell, narrowing the gap between voltage threshold (VT) distributions, resulting in voltage shifts and causing bit errors due to cell-to-cell interference.
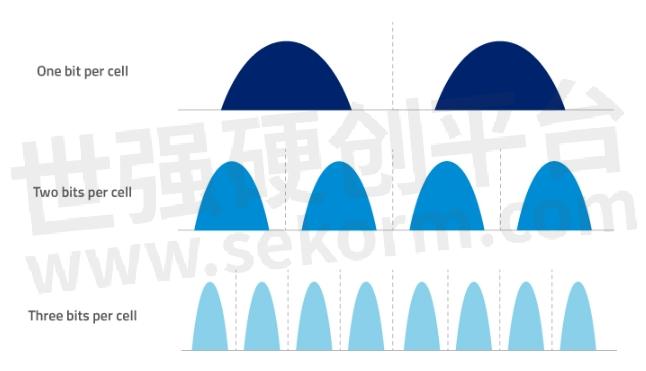
Figure 2. More bits stored per cell deliver increased density/capacity, but also increases cell-to-cell interference, as cells get crammed more closely together. A read or write to one cell may impact other neighboring cells, and cause bit errors.
Error Detection and Correction in ATP NAND Flash Storage Devices
Error correction codes (ECC) are techniques used to correct errors in the NAND flash, allowing recovery of data that may be corrupted due to bit errors. Internal ECC mechanisms can detect/correct up to a certain number of errors.
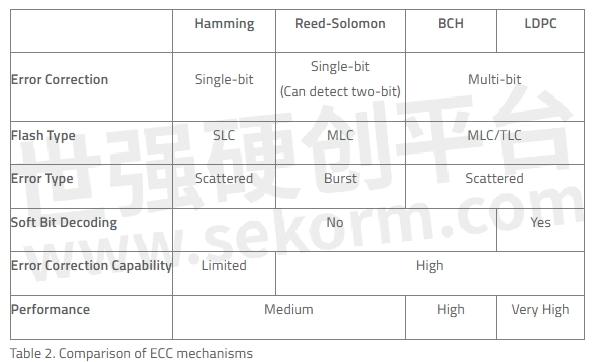
An example of ECC employed by other flash storage products is the Hamming Code. Invented in 1950 and named after its inventor, Richard Hamming, this algorithm can detect and correct 1-bit errors but can only detect and not correct 2-bit errors. It is easy to implement due to its limited error correcting abilities and is widely used in single-level cell (SLC) flash, which is simpler in architecture and only requires single-bit ECC. A popular Hamming code is 7, 4 where, in a 7-bit block, only 4 bits are made up of data and the other 3 bits are error correction codes.
Below is a sample implementation of the Hamming Code on a 2 KB page with 2048 bytes of user data. (In flash storage devices where page size is over 512 bytes, the data is divided into sections of 512 bytes with a Hamming code used for each 512-byte section.
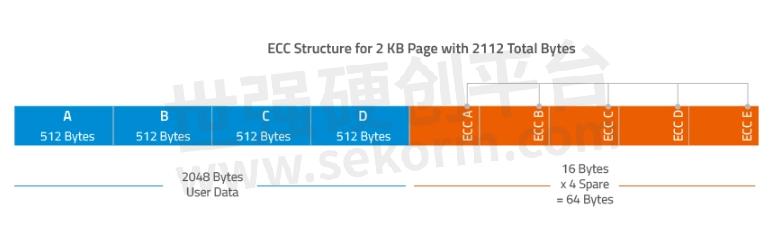
Figure 3. Sample Hamming Code implementation for a 2 KB page. The Hamming Code for each 512 KB section is stored in the Spare area.
While some products available in the market use only simple Hamming codes, ATP products employ
advanced ECC that can correct multiple bit errors.
The following section introduces the error detection and correction mechanisms applied in ATP's flash storage devices:
Reed-Solomon Algorithm
Invented in 1960 by engineers Irving Reed and Gustave Solomon, both engineers at MIT's Lincoln Labs, the Reed-Solomon algorithm involves the addition of extra/redundant data to a block of digital data. It is commonly used in hard disk drives and compact discs, as well as NAND flash storage where it is often used to handle NAND flash bit-flipping. A bit flip occurs when an operation on one cell causes disturbances on another cell due to the proximity of memory cells built too close to each other. When a bit flip happens, the floating gate of a cell may gain (get programmed) or lose (get erased) electrons due to the disturbance in another cell.
Reed-Solomon codes correct symbols and is thus considered excellent for applications where errors tend to be clustered together. The Reed-Solomon algorithm is widely used to correct multiple-bit errors in a single page but may perform poorly with large message blocks, greatly amplifying the time to encode or decode the data when the block size is doubled.
A popular Reed-Solomon code is RS (255, 247) with 8-bit symbols. Each code word contains 255 code word bytes, of which 247 bytes are data and 8 bytes are parity. The decoder can correct any 4 symbol errors in the code word.
Currently, some ATP flash products implement Reed-Solomon encoding using a 4-byte-on-512-byte encoding. This means the ECC mechanism on these products can correct at least 4 bits error for every 512B. However, in a best-case scenario, it can correct up to 32 bits error per 512B, as long as these 32 bits error are located within same 4 symbols.
BCH (Bose, Chaudhuri, Hocquenghem) Algorithm
BCH codes were invented in 1959 by Alexis Hocquenghem, and independently in 1960 by Raj Bose and D.K. Ray-Chaudhuri. BCH codes can correct multiple-bit errors and can handle both random and burst errors. The main advantage of BCH codes is that they can be easily decoded using a method called "syndrome decoding." BCH codes require a low amount of redundancy and are widely used in satellite communications, compact disc drives and bar codes.
In contrast to the Reed-Solomon algorithm, which provides more robust error correction ability but requires a large amount of system resources to implement, the BCH algorithm is becoming popular because of its improved efficiency, being able to detect both highly concentrated and widely scattered errors. Another advantage is that the encoding and decoding techniques are relatively simple and BCH codes require a low amount of redundancy.
LDPC (Low Density Parity Check)
LDPC codes, also known as Gallagher codes in honor of its developer Robert G. Gallagher, are powerful error correcting algorithms first proposed in the 1962 PhD thesis at MIT but have been gaining wide implementation only about 10 years ago. They are increasingly being used in the enterprise world for their ability to decode both soft-bit data and hard-bit data. In Gallagher's thesis, low density parity code is defined as "a linear binary block for which the parity check matrix of interest has a low density of ones," meaning there are fewer 1s compared to the 0s).
Advantages of LDPC over other algorithms:
Low decoding complexity
Uses both hard-bit and soft-bit information from the NAND flash during decoding
Demonstrates good performance with short blocks
Delivers "near-capacity" performance with long blocks. (Near capacity refers to the Shannon limit, which is the maximum rate at which data can be sent over a channel with close to or approaching zero error.)
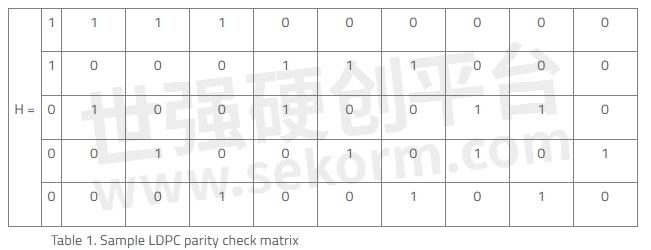
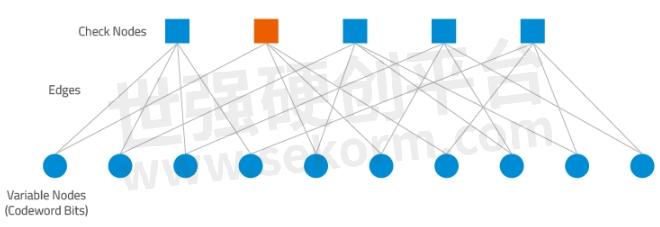
Figure 4. A Tanner graph shows a graphical representation of the LDPC code for the given parity check matrix in Table 1 and helps describe the decoding algorithm. "Check Nodes" represent the number of parity bits, and "Variable Nodes" represent the number of bits in a codeword. An edge connects a bit node to a check node only if the bit is included in the parity check.
Summary
The following table provides a comparison of the ECC algorithms discussed in this article.
(Source: Error Correction Codes in NAND Flash Memory)
As NAND flash lithography scales down, cell geometries shrink and cells store more bits per cell, densities increase but so do error bits. To ensure the reliability of its industrial flash storage products, ATP employs advanced error detection and correction technologies.
- |
- +1 赞 0
- 收藏
- 评论 0
本文由涂抹转载自ATP Blogs,原文标题为:https://www.atpinc.com/blog/ldpc-ssd-low-density-parity-check-ecc-algorithm,本站所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源,不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
相关研发服务和供应服务
相关推荐
How Wear Leveling Increases SSD Lifetime?
Wear leveling is needed to address the finite program/erase capability of NAND flash memory cells. When only a limited number of blocks are repeatedly used, the device can prematurely wear out. By even distributing the program/erase cycles over the entire flash storage device, the ATP Enhanced Wear Leveling mechanism makes sure that all memory cells are used to the maximum, thereby extending the life span of the device.
How Temperature Affects Data Retention for SSDs
How can the integrity of data written on the flash drive be guaranteed at high operating or storage temperatures?
SSD Endurance: Challenges and Solutions
In this article, we will look at some factors affecting SSD life expectancy and how these can be addressed to manage SSD endurance.
ATP(华腾国际)DRAM存储模块和NAND闪存产品选型指南(英文)
目录- Company Profile Segment Challenges and Solutions Thermal Solutions Endurance Solutions Security Solutions CFexpress & USB 3.0 Value Line SSDs DDR5 DRAM SOLUTIONS FLASH SOLUTIONS Flash Products Naming Rule Solutions & Technologies Flash Technology Overview table Complete Flash Spec Overview & Product Dimensions
型号- A750PI,E650SC SERIES,S600SC,B800PI,S750 SERIES,S600SI,S600SCA,E750PC SERIES,B600SC,N700PC,S700SC,E650SC,A750 SERIES,E600VC,S800PI,A750PI SERIES,I800PI,A600VC,A650SI,A650SC,N700 SERIES,S650SI,N750,N750PI,A800PI,A700PI,N700SI,N650 SERIES,E600SAA,N700SC,A750,N600SC,A600VC SERIES,E600SA,E650SI,E650SI SERIES,N750 SERIES,E700PIA,TR-03153,N600SI,S650,S650SC,E700PAA,N650SIA,E600SI,B600SC SERIES,S750SC,S600SIA,I700SC,N650SI,N600VI,E600SIA,E750PI,N650SC,N750PI SERIES,N600VC,I600SC,E750PC,S700PI,A650 SERIES,N650,N600 SERIES,N600VC SERIES,S650 SERIES,A650,AES-256,E700PI,A600SI,E750PI SERIES,N700PI,E700PA,S750,S750PI,E700PC,A600SC
ATP Launches Its Tiniest PCIe Gen3 x4 NVMe™ SSDs in M.2 Type 1620 HSBGA Package
ATP Electronics, the global leader in specialized storage and memory solutions, has announced the launch of its tiniest NVMe flash storage offering: the N700 Series PCIe® Gen3 x4 NVMe™ solid state drives (SSDs, which are available as M.2 Type 1620 heatsink ball-grid array (HSBGA) package.
ATP(华腾国际)固态硬盘选型指南
描述- Since 1991, we have consistently distinguished ourselves as one of the world’s leading original equipment manufacturers (OEM) of high-performance, high-quality and high-endurance NAND flash products and DRAM modules.
型号- A750PI,S600SC,B800PI,S750 SERIES,S600SI,B600SC,N700PC,A750 SERIES,E650SC,N601,N651SI,A600VI,S800PI,E600VC,I800PI,A600VC,A650SI,A650SC,N651SC,N750,S650SI,A600VI SERIES,N750PI,N651SIE,A800PI,N601 SERIES,A700PI,N651SIA,N650 SERIES,E600SAA,A750,A600VC SERIES,N600SC,E600SA,E650SI,N750 SERIES,E700PIA,N600SI,S650,S650SC,N651SI SERIES,E700PAA,B600SC SERIES,E600SI,N600VI SERIES,I700SC,N600VI,N650SI,E600SIA,N650SC,E750PI,N600VC,I600SC,E750PC,N651,S700PI,A650 SERIES,N650,N751PI,S700PC,N600VC SERIES,N651 SERIES,S650 SERIES,A650,N601SC,S750PC,E700PI,A600SI,N700PI,E700PA,S750,S750PI,E700PC,N651SCE,A600SC
Bringing 3D TLC NAND Flash Endurance and Reliability Closer to SLC/MLC
The advent of 3D NAND technology allowed for more relaxed lithography and broke planar NAND limitations. By stacking cells vertically, 3D NAND flash increased drive reliability and endurance. ATP breaks new ground with its new 3D TLC-based SATA SSDs.
The ATP Gym and Coach System: Exercising SSDs to Ensure Total Fitness
With the Gym and Coach system, ATP has dramatically improved RDT and the initialization process for functional test details. By making industrial SSDs undergo a lot of “painful” exercises through stringent testing, ATP makes sure that customers have everything to gain by receiving the most robust, reliable and enduring flash storage products for their applications.
ATP Exhibits at Embedded World 2024
Participants should not miss a visit to ATP’s Booth in Hall 1-210, where ATP once again demonstrates its commitment to redefine memory and data storage reliability, scalability, and efficiency. Attendees to Embedded World 2024 can expect to see a new breed of flash storage solutions with ATP’s 176-layer NAND flash innovation, industrial enterprise-readiness for Edge computing and artificial intelligence, and latest DDR5-5600 memory offerings.
SSD End-of-Life Validation Test: Ensuring Reliability, Endurance and Retention From 0% to 100% and Beyond EOL
ATP’s EOL Validation Test is just one of the many reliability and endurance tests developed and performed by ATP to ensure strict compliance to the highest standards of quality. ATP is committed to delivering high-performance and high-endurance NAND flashes storage products to ensure the best value for a total cost of ownership (TCO).
ATP‘s PCB Assembly Solderability Validation Tests
ATP’s PCB assembly validation tests are part of the many reliability and endurance tests developed and performed by ATP to ensure strict compliance to the highest standards of quality. ATP is committed to delivering high-performance and high-endurance NAND flashes storage products to ensure the best value for the total cost of ownership (TCO).
CompactFlash card The Global Leader in Specialized Storage and Memory Solutions
型号- I700SC,I800PI,I600SC
【应用】ATP推出32G eMMC AF032GEC5X-SEK0511用于V2X系统,适用温度-40~85℃
V2X系统旨在通过允许车辆与几乎所有可检测的东西进行通讯来提高车辆的安全性,舒适性和便利性。在系统设计中需要用到eMMC进行数据存储,在此选用的ATP的32G Bytes的eMMC AF032GEC5X-SEK0511替换NAND FLASH。
BGA SSD: Powerful NVMe Performance in a Tiny Package
ATP‘s N700 Series SSDs are built with 3D triple-level cell (TLC) configured as pseudo-single-level cell (pSLC) NAND flash. By storing only one bit per cell, they increase the reliability and endurance of the NAND flash memory, while benefiting from the lower cost compared with native SLC, due to the higher cell density.
IoT and IIoT: Flash Storage, Sensors and Actuators in Cloud/Edge
For data in the cloud or at the edge, ATP offers industrial-grade flash storage solutions that meet stringent endurance, retention and reliability requirements of IoT/IIoT. As a member of the Intel® Internet of Things Solutions Alliance, ATP is a qualified IoT/IIoT hardware manufacturer offering memory and storage solutions designed to meet the growing needs and challenges of a connected world.
电子商城
现货市场
服务
可烧录MCU/MPU,EPROM,EEPROM,FLASH,Nand Flash, PLD/CPLD,SD Card,TF Card, CF Card,eMMC Card,eMMC,MoviNand, OneNand等各类型IC,IC封装:DIP/SDIP/SOP/MSOP/QSOP/SSOP/TSOP/TSSOP/PLCC/QFP/QFN/MLP/MLF/BGA/CSP/SOT/DFN.
最小起订量: 1 提交需求>
拥有IC烧录机20余款,100余台设备,可以烧录各种封装的IC;可烧录MCU、FLASH、EMMC、NAND FLASH、EPROM等各类型芯片,支持WIFI/BT模组PCBA烧录、测试。
最小起订量: 1 提交需求>










































































































































































































登录 | 立即注册
提交评论